How to create a data model in Django
In Django, models is a built-in Python class that is used to create tables, their fields, and various constraints. Each model is a subclass of the django.db.models.Model class and maps to a single table in a database. Each attribute of the model represents a database field.
How to create a model
Every Django app has a models.py file where the models are created. The code snippet below creates a simple model named Product that has two fields, name and price:
from django.db import models
class Product(models.Model):
name = models.CharField(max_length=50)
price = models.IntegerField()
Explanation
-
The
modelsclass is imported fromdjango.dband creates a classProductthat acceptsmodels.Modelas an argument. -
CharFieldstores values that are ofstringtype and accepts a required parametermax_lengththat specifies the maximum allowed length of the input. -
IntegerFieldstores values that are of theintegertype.
How to map a model to a table
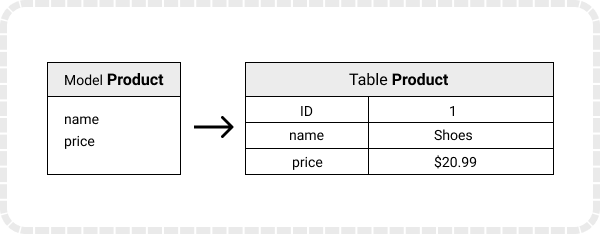
Django maps the fields defined in Django models into table fields of the database. While mapping, Django will create an ID field by itself.
Below is an illustration of how mapping works:
Whenever you create, update, or delete a model, you need to run two commands in any of the models.py files of the project:
make migrations: This command generates aSQL Structured Query Language
Make sure to add the project in preinstalled apps in
settings.py.
python manage.py makemigrations
migrate: This command creates the table in our database.
python manage.py migrate
The commands above create a model and map it onto a table. With this, you are all set to add, delete, update, or read data from your database.