How to create a Python GUI
Overview
Have you ever written a Python program and wished to display the output in a fancy and well-designed user interface?
Several GUI packages/frameworks are used to create appealing user interfaces for our Python desktop programs in Python. Some of these frameworks/packages include:
- PySide 2
- Wxpython
- Kivy
- PyQT5
- Tkinter and more
Amongst all of the GUI frameworks and packages used in Python today, Tkinter is the only one that comes with the Python standard library and needs no installation. All you need to do is get it imported into your script, and you are good to go.
For the other frameworks, you have to install them and check out their documentation from their providers before using them in your script.
To install any GUI frameworks/packages, you need to run the following command:
pip install gui_package_name
Also check their documentation on how to use it.
In this shot, we will learn to create a simple GUI using Python Tkinter.
Code example 1
In the code below, the tkinter module was imported from the Python standard library at line 2 to make the tkinter modules available for use in the script. Moving onward, we are creating a simple GUI screen, specifying the name and giving it width and height. Lastly, we are adding the mainloop() method to the code so that tkinter can create the required GUI for us.
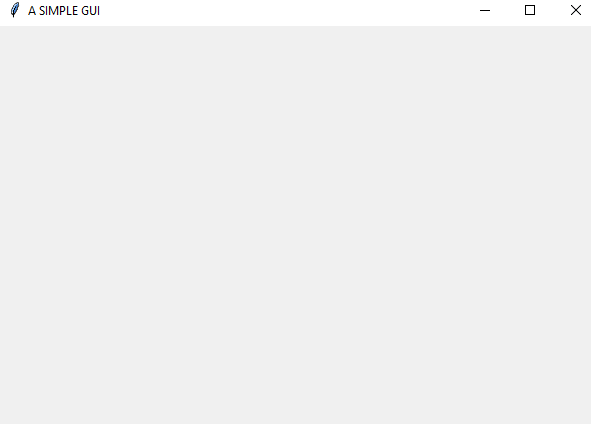
#import the tkinter moduleimport tkinter as tk# create a simple screen and save to window variablewindow = tk.Tk()# give the GUI a namewindow.title('A SIMPLE GUI')# give a height and legnthwindow.geometry('600x400')# always include this line to let your code runwindow.mainloop()
Output
Below is the output of the above-given code on a Windows OS. It will be the same for other OS, only with some minor differences.
Now, let’s add some widgets. Some of these widgets include:
- Label
- Button
- Canvas
- Checkbutton
- Frame
- Menu
And the list goes on.
Code example 2
Below is the code in which some new lines were added. These new lines will create the Label widget, using the tk.Label command. The Label made below in the code has the foreground and background colors and specified height and width.
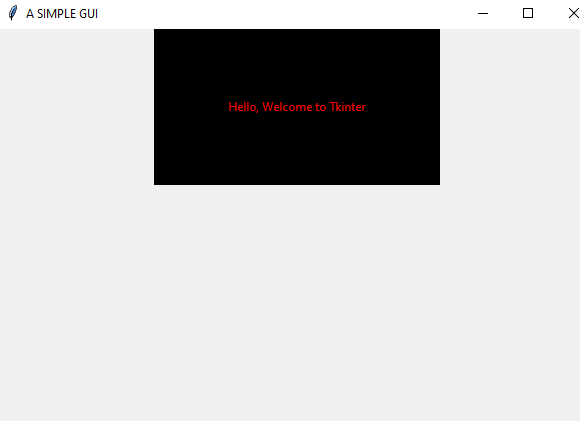
#import the tkinter moduleimport tkinter as tk# create a simple screen and save to window variablewindow = tk.Tk()# give the GUI a namewindow.title('A SIMPLE GUI')# give a height and legnthwindow.geometry('600x400')# add a label and some design as wellwelcome = tk.Label(text="Hello, Welcome to Tkinter"fg="red", #foregroundbg="black", #backgroundwidth=40,height=10)#adding the widget to the windowwelcome.pack()# always include this line to let your code runwindow.mainloop()
Output
The image below is the new output from the code that was modified.
You can add as many widgets as you want by using the Tkinter module library you have imported by typing Tkinter.widget_name in your script. You can do several other things to this GUI to get what fits your needs. To learn more, visit the available Tkinter documentation.