How to implement Data Block API
Data block API is a high-level API in fastai that is expressive for data loading. It is a way to systematically define all of the steps necessary to prepare data for a Deep Learning model and give users a “mix and match” recipe book to use when combining these pieces. In this shot, we’ll be diving into the code.
Let’s dive directly into the code:
!pip install -q fastai2
Depending on the type of problem, blocks in the data blocks may change and the rest will remain the same. Let’s see our first example:
from fastai2.vision.all import *
Mask Block
path = untar_data(URLs.CAMVID_TINY)
camvid = DataBlock(blocks=(ImageBlock, MaskBlock(codes = np.loadtxt(path/'codes.txt', dtype=str))),
get_items=get_image_files,
splitter=RandomSplitter(),
get_y=lambda o: path/'labels'/f'{o.stem}_P{o.suffix}',
item_tfms = Resize(224),
batch_tfms=aug_transforms())
dls = camvid.dataloaders(path/"images")
dls.show_batch()
Here we have created MaskBlock in blocks.
Depending on the tasks blocks = () change, lock’s are used to help nest transforms inside of a pre-defined problem domain.
There are different types of blocks:
- ImageBlock is used if the dataset is made up of images
- CategoryBlock is for single-label categorical targets
- MultiCategoryBlock is for multi-label categorical targets
- RegressionBlock is for float targets
- MaskBlock is for segmentation masks, potentially with codes
- PointBlock is for points in an image
- BBoxBlock is for bounding boxes in an image
- BBoxLblBlock is for labeled bounding boxes, potentially with vocabulary
So, coming back to our example, the MaskBlock is generated with codes that give a correspondence between the pixel value of the masks and the object they correspond with.
Multi-label classification problem
Now, let’s take a look at the the multi-label classification problem:
path2 = untar_data(URLs.PASCAL_2007)
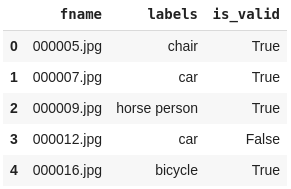
df = pd.read_csv(path2/'train.csv')
df.head()
pascal = DataBlock(blocks=(ImageBlock, MultiCategoryBlock),
splitter=ColSplitter('is_valid'),
get_x=ColReader('fname', pref=str(path2/'train') + os.path.sep),
get_y=ColReader('labels', label_delim=' '),
item_tfms = [FlipItem(p=0.5),Resize(224,method='pad')],
batch_tfms=[*aug_transforms(do_flip=True, flip_vert=True, max_rotate=180.0, max_lighting=0.6,max_warp=0.1, p_affine=0.75, p_lighting=0.75,xtra_tfms=[RandomErasing(p=1.0,sh=0.1, min_aspect=0.2,max_count=2)]),Normalize])
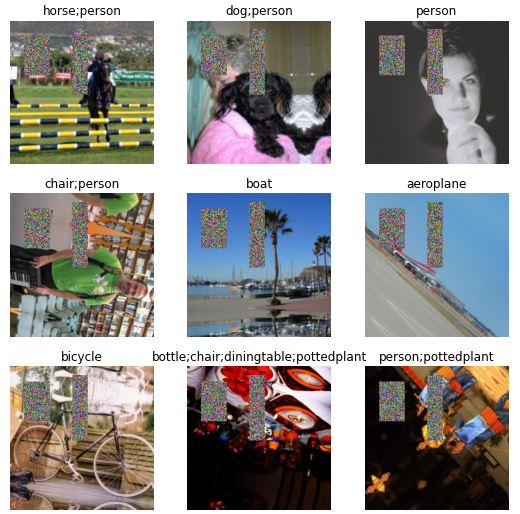
dls2 = pascal.dataloaders(df)
dls2.show_batch()
Here, the basic principles remain the same depending on which domain blocks are used.
Now, we saw splitters in the first example since we used RandomSplitter and did not have any rule on how to split the data. However, this is not the case in the second example. In the second example, we have a column called is_valid in df. So, depending on that column, we can determine whether we need to split, so ColSplitter(‘is_valid’) is used.
Free Resources
- undefined by undefined