How to install Julia packages via command line
Julia is a programming language suitable for mathematical and computational analysis in data science and machine learning fields. The Julia ecosystem consists of thousands of packages created to perform specific tasks ranging from visualization, computer vision, mathematical computation, as well as machine learning.
To use a package, we need to install it first. There are two ways we can do this on the command line:
- Install by importing Julia’s package manager,
Pkg. - Install directly or interactively while on REPL mode.
In this article, we’ll focus on how to install a package in Julia, using these two methods.
Installing using Pkg
Pkg is the package manager for Julia which handles installation, updates, and removal of packages.
-
Identify the package you need. For example, if you need to read a csv file into a data frame, the
Queryversepackage will suffice. -
Use
importto importPkg.
import Pkg
- Use
Pkgto install your package.
Pkg.add("Queryverse")
- Use the package.
using Queryverse
df = DataFrame(load("mydata.csv"))
Installing multiple packages
To install multiple packages, use the .dot notation to provide a list of packages, as shown below.
Pkg.add.(["CSV","Plots"])
Installing unregistered or custom packages.
Installing a package that is not registered is also possible in Julia. All you have to do is provide the URL to the custom package, such as a GitHub repo link. To learn how to create a custom package, click this article.
Pkg.add("url_to_custom_package/example.jl")Installing a package interactively on Julia’s REPL
Julia’s commandline comes with an interactive mode called the REPL.
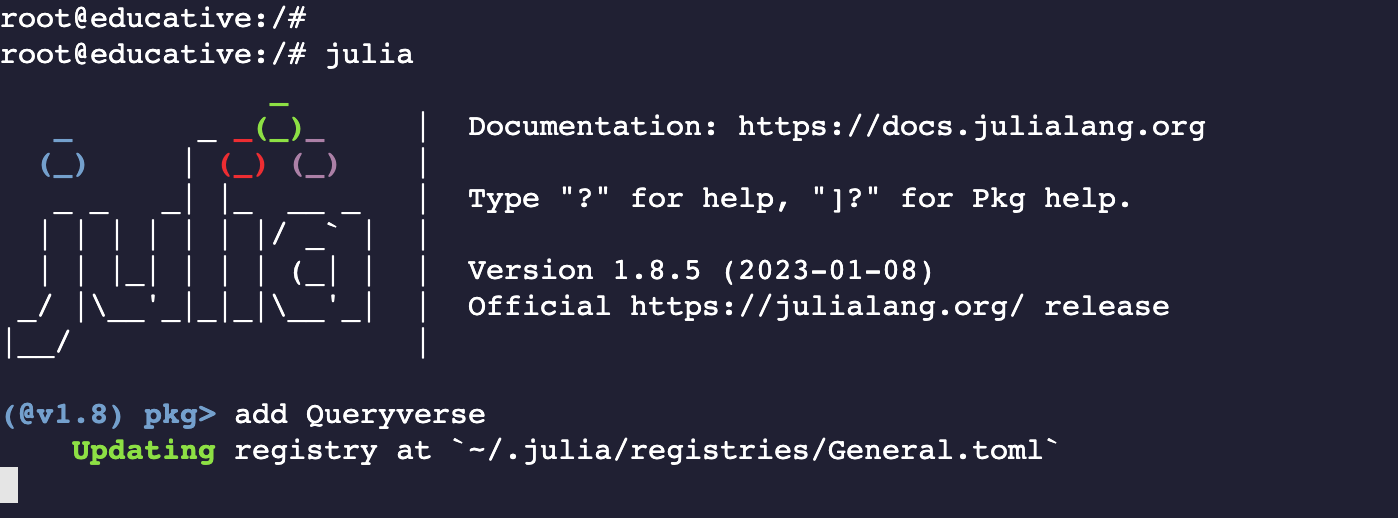
We can use the REPL to install a package. All we have to do is type a closing bracket ], to enter REPL mode and then proceed. For example, to install Queryverse, type in ] and then use the keyword add.
add Queryverse
This is shown below:
Note: Use the terminal below to install a package. Simply type Julia to start.
Free Resources