How to perform URL routing in Django
A web application consists of multiple pages and each page has its own route. A route can be defined as a
Django lets us route URLs however we want and with no framework limitations. In this shot, we will see how we can create our own URL in Django.
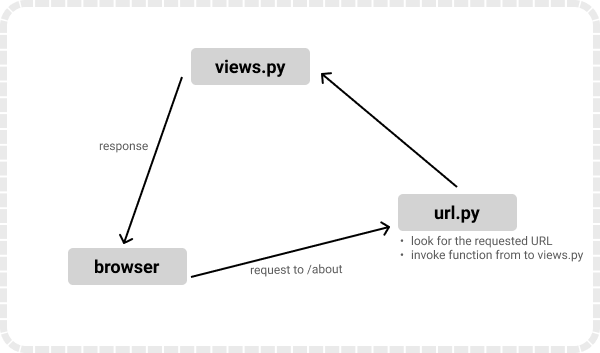
URL routing flow
As we can see, the user enters a URL in the search bar of the web browser. Then, that URL is passed to the url.py file where it tries to find a matching URL pattern. If a matching URL is found, the corresponding view function attached with that URL is invoked. Otherwise, it returns 404.
How to create a new route
The routes are defined in the url.py file that can be either at the project or application level. We will focus on creating our route at the project level.
To create a route in Django, we will use the path() function that accepts two parameters: a URL and a View function.
- Initially, the
url.pyfile looks like this:
from django.contrib import admin
from django.urls import path
urlpatterns = [
path('admin/', admin.site.urls),
]
-
All the routes are created inside the
urlpatternslist. -
Simply add a new path as below and a new route will be created.
from django.contrib import admin
from django.urls import path
from . import views
urlpatterns = [
path('admin/', admin.site.urls),
path('about/', views.about),
]
-
With this, the
aboutpath will become a possible extension to the website’s URL. Assuming we’re using localhost and a port of8000, it would be127.0.0.1:8000/about/to access this new URL. -
When this new URL is entered in the browser, it will check for a matching route. In this case, it will invoke the
aboutmethod fromviews.py. -
The
views.pyfile may look something like this:
from django.shortcuts import render
from django.http import HttpResponse
def about(request):
return HttpResponse('<h1>This is about me!.</h1>')
Note: We can also create nested routes or even hundreds of routes all into this single
urlpatternslist.
Conclusion
The steps above give a brief explanation of how URL routing works in Django. It is quite easy, provided that we know its structure and the flow of events that occur when a specific URL is to be accessed.