How to test your Laravel application's views
Laravel is a full-stack framework that has many components, from routing, to middlewares, to views. Manually testing each of these components is very stressful and not very efficient. Laravel provides an easy way to test our application. Laravel’s feature tests let you make HTTP requests to your application and examine the response.
To get started, use the laravel installer to create a Laravel application.
laravel new testy
-
Now, the application bootstraps with a test directory that has the
FeatureandUnitsub-directories. In this shot, we will create a feature test to examine our application’s views. -
Next, you want to create a basic view to list users of the application. For this view to list users, you must have users on your application.
-
To retrieve users, update the
DatabaseSeeder.phpseeder file’srunmethod to contain the following:
User::factory(20)->create();
This creates 20 fake users when run.
- Now, seed the database.
php artisan db:seed
- Update the
web.phpfile to fetch all users and pass them to the view.
Route::get('/', function () {
return view('welcome')->with('users', User::all());
});
- Now, the list of users can be rendered as follows:
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
<link href="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/bootstrap@5.1.1/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css" rel="stylesheet" integrity="sha384-F3w7mX95PdgyTmZZMECAngseQB83DfGTowi0iMjiWaeVhAn4FJkqJByhZMI3AhiU" crossorigin="anonymous">
<title>Hello, world!</title>
</head>
<body>
<table>
<caption>Users</caption>
<thead>
<tr>
<th scope="col">ID</th>
<th scope="col">Name</th>
<th scope="col">Email</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
@forelse($users as $user)
<tr>
<th scope="row">{{ $user->id }}</th>
<td>{{ $user->name }}</td>
<td>{{ $user->email }}</td>
</tr>
@empty
<p>No registered user</p>
@endforelse
</tbody>
</table>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/bootstrap@5.1.1/dist/js/bootstrap.bundle.min.js" integrity="sha384-/bQdsTh/da6pkI1MST/rWKFNjaCP5gBSY4sEBT38Q/9RBh9AH40zEOg7Hlq2THRZ" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
</body>
</html>
- Finally, we can create the test to test the view.
- Run
php artisan make:testto create a feature test.
php artisan make:test UsersTest
-
Here, we create a test named
UsersTest. This creates a new file,UsersTest.php, in thetests/Featuredirectory. -
Now, we need to update the test to match our needs. The test methods are usually named as
test_, followed by the action name. So, in this case, rename it totest_users_list. -
Notice how the application makes a get request to
/by default and checks if the response status is200. -
The
assertStatusmethod is used to check if the response code matches a given code. -
To check if the response matches 200 exactly, you can use the
assertOkmethod instead. -
To check if a given text is on the page, i.e., to see if a user is listed, use
assertSee.
$response = $this->get('/');
$user = User::first();
$response->assertSee($user->name);
- You can also check if a given string is not displayed with
assertDontSee.
$response->assertDontSee('Alfred');
- You may also use
assertViewHasto check if data is passed into the view.
$response->assertViewHas('users', User::all());
- You can even check if the correct view was rendered with
assertViewIs.
$response->assertViewIs('welcome');
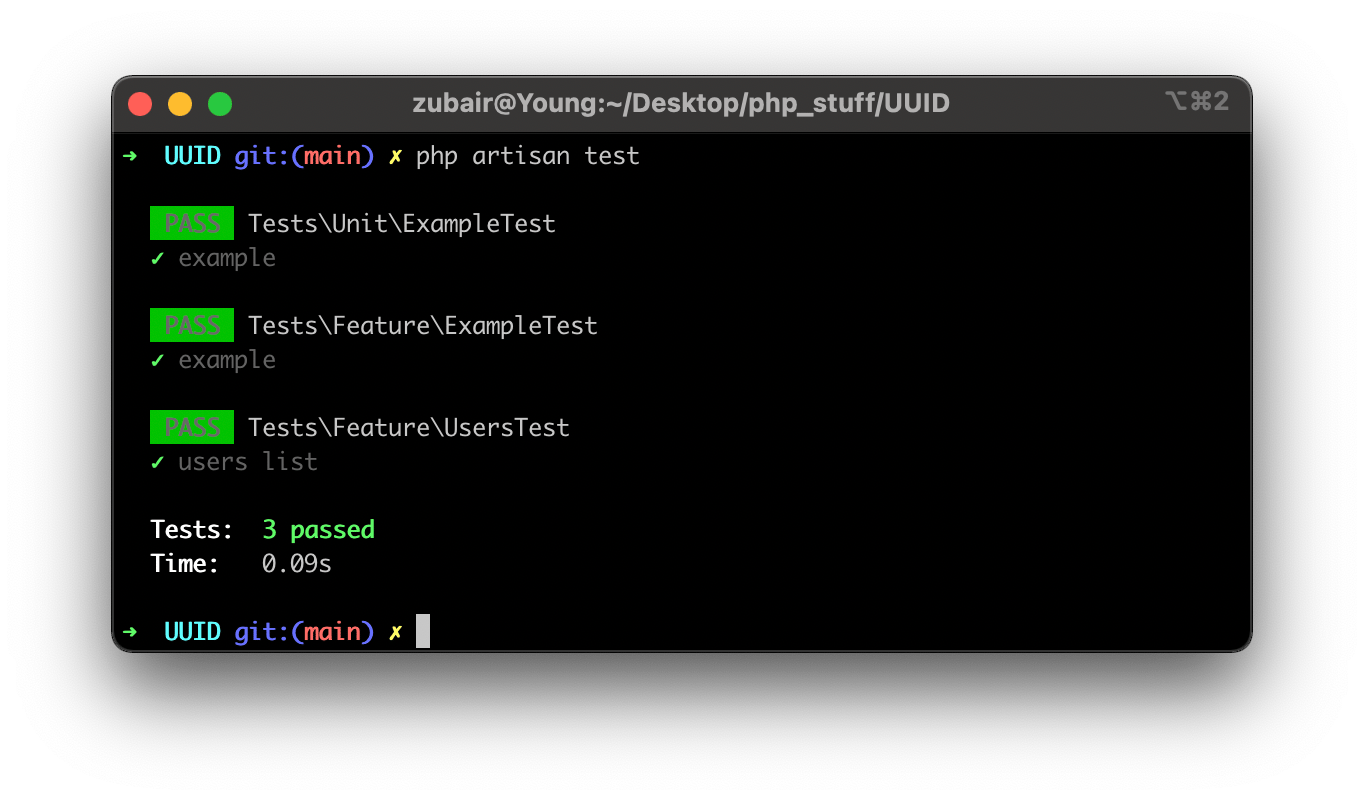
Laravel has many more methods to test database actions and API responses. To run these tests, run the following code in the terminal:
php artisan test