String compression using run length encoding
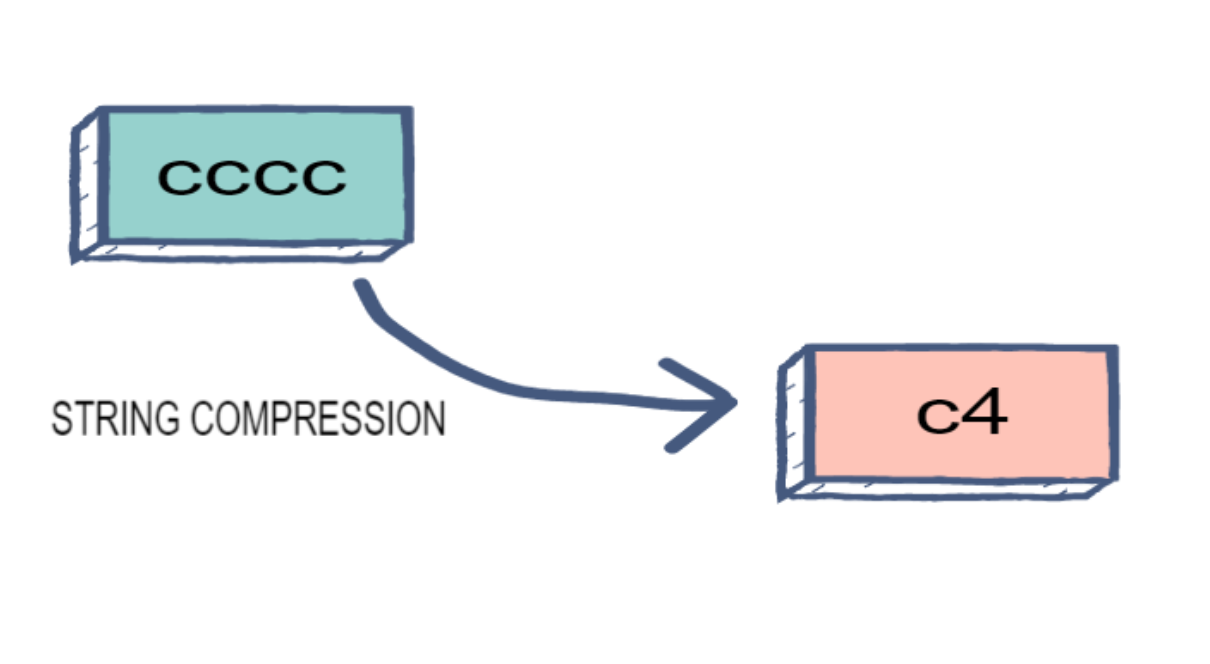
“String Compression Algorithm” or “Run Length Encoding” happens when you compress a string, and the consecutive duplicates of each string are replaced with the character, followed by the consecutive, repeated character count.
For example:
After string compression, the string “aaaabbcddddd” would return “a4b2c1d5”.
You may not have seen such strings in texts, but image and video files almost always have long repeating sequences. Some uses of run-length encoding include:
- Compressing faxed documents
- Compressing JPEG images
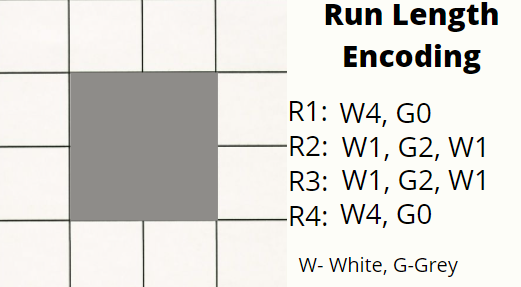
In images, colors are replaced by the character, or color, followed by the number of times that color repeats itself. This is shown below:
Steps for string compression using run-length encoding:
-
Start by taking the first character of the given string and appending it to the compressed string.
-
Next, count the number of occurrences of that specific character and append it to the compressed string.
-
Repeat this process for all the characters until the end of the string is reached.
Code
This is how the code would be implemented:
#include<iostream>#include <string>using namespace std;void compress(string s){int num = s.length(); //calculating length of the stringint i=0;while ( i < num) {// Counting the repetitions of each characterint repetition = 1;while (s[i] == s[i+1] && i < num-1 ) {repetition++;i++;}// Print character and its countcout << s[i] << repetition;i++;}}int main(){string str = "aaaabbcddddd";compress(str);}
Some run-length encoding approaches also use an escape character before the count value. For example, if the file has some numeric character. With the escape character approach, the string compression of “aaaabbcddddd” would return “aa4bb2cdd5”.
#include <iostream>#include <string>using namespace std;void compress(string s){int num = s.length(); // calculating length of the stringint i = 0;while (i < num){// Counting the repetitions of each characterint repetition = 1;while (s[i] == s[i+1] && i < num - 1){repetition++;i++;}// Print character and its count using the escape character approachcout << s[i];if (repetition > 1){cout << s[i] << repetition;}i++;}}int main(){string str = "aaaabbcddddd";compress(str);return 0;}
Line 12: The
repetitionvariable is initialized to1to count the occurrences of each character.Lines 13–17: While the current character is the same as the next character and the end of the string hasn't been reached, the repetition count is incremented, and the index
iis incremented to move to the next character.Lines 21–25: After counting consecutive occurrences, the current character is printed. If the repetition count is greater than
1, the character is printed again followed by its count, representing the escape character approach for run-length encoding. Finally, the indexiis incremented to move to the next character in the string.
Refreshing your basic string compression concepts
What is the compressed form of the string “wwggmmmmmk”?
w2g2m5k1
w1g2m4k1