Three ways to combine DataFrames in Pandas
Pandas join() function
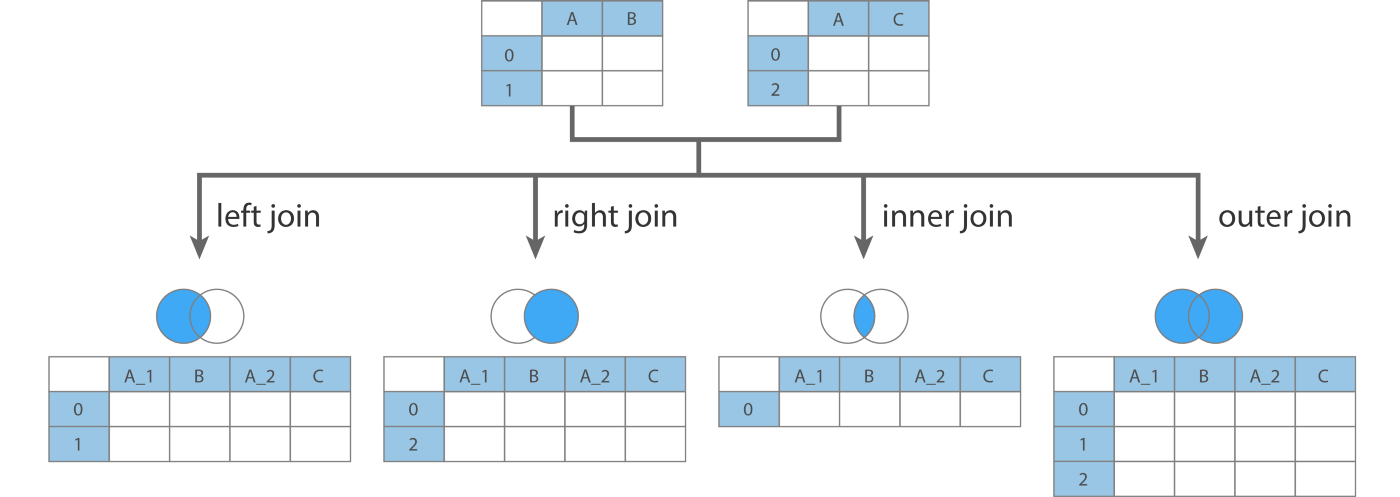
This function allows the lowest level of control. It will join the rows from the two tables based on a common column or index. Have a look at the illustration below to understand various type of joins.
Now, let’s have a look at the coding part.
df1 = pd.DataFrame({'key': ['K0', 'K1', 'K2', 'K3', 'K4', 'K5'],'A': ['A0', 'A1', 'A2', 'A3', 'A4', 'A5']})df2 = pd.DataFrame({'key': ['K0', 'K1', 'K2'],'B': ['B0', 'B1', 'B2']})print(df1)print(df2)
The output of the above code snippet is:
key A
0 K0 A0
1 K1 A1
2 K2 A2
3 K3 A3
4 K4 A4
5 K5 A5
key B
0 K0 B0
1 K1 B1
2 K2 B2
Now, let’s join the two DataFrames.
df1.join(df2, lsuffix='_caller', rsuffix='_other')
The output of the above join operation will be:
key_caller A key_other B
0 K0 A0 K0 B0
1 K1 A1 K1 B1
2 K2 A2 K2 B2
3 K3 A3 NaN NaN
4 K4 A4 NaN NaN
5 K5 A5 NaN NaN
Explanation :
- By default,
join()does a left join, but you can change the type of join by providing a value for thehowparameter in thejoin()function ashow='type_of_join' - The parameter
lsuffixis the suffix that will be added to the column name from the left frame’s overlapping columns. - The parameter
rsuffixis the suffix that will be added to the column name from the right frame’s overlapping columns.
Pandas merge() function
This function is also used to combine or join two DataFrames with the same columns or indices. More or less, it does the same thing as join().
However, merge() allows us to specify what columns to join on for both the left and right DataFrames.
merge() is useful when we don’t want to join on the index.
df1 = pd.DataFrame({'lkey': ['foo', 'bar', 'baz', 'foo'],'value': [1, 2, 3, 5]})df2 = pd.DataFrame({'rkey': ['foo', 'bar', 'baz', 'foo'],'value': [5, 6, 7, 8]})print(df1)print(df2)
The output of the above code is:
lkey value
0 foo 1
1 bar 2
2 baz 3
3 foo 5
rkey value
0 foo 5
1 bar 6
2 baz 7
3 foo 8
Now, let’s merge the two DataFrames.
df1.merge(df2, left_on='lkey', right_on='rkey')
The output of the above code is:
lkey value_x rkey value_y
0 foo 1 foo 5
1 foo 1 foo 8
2 foo 5 foo 5
3 foo 5 foo 8
4 bar 2 bar 6
5 baz 3 baz 7
Explanation:
- The parameter
left_onis the column or index level names to join on in the left DataFrame. - The parameter
right_onis the column or index level names to join on in the right DataFrame. - By default, the
merge()function performs an inner join, but you can change it by passing the parameter valuehow='type_of_join'.
Pandas concat() function
This function is used to append one (or more) DataFrames stacked below the other (or sideways, depending on whether the axis option is set to 0 or 1).
Also, make sure that the dimensions of the DataFrames should match along the axis while concatenating.
df1 = pd.DataFrame({'Key': ['b', 'b', 'a', 'c', 'a', 'a', 'b'],'data1': range(7)})df2 = pd.DataFrame({'Key': ['a', 'b', 'd'],'data2': range(3)})print(df1)print(df2)
The output of the above code is:
Key data1
0 b 0
1 b 1
2 a 2
3 c 3
4 a 4
5 a 5
6 b 6
Key data2
0 a 0
1 b 1
2 d 2
Now, let’s concatenate the DataFrames.
pd.concat([df1, df2])
The output of the above code is:
Key data1 data2
0 b 0 NaN
1 b 1 NaN
2 a 2 NaN
3 c 3 NaN
4 a 4 NaN
5 a 5 NaN
6 b 6 NaN
0 a NaN 0
1 b NaN 1
2 d NaN 2
Explanation:
- The dataframe
df2is appended afterdf1. NaNvalues denote that the values for that column are not present in the DataFrame.
Which to use and when to use?
- The
join()method works best when we are joining DataFrames on their indexes. - The
merge()method is more versatile and allows us to specify columns, besides the index to join on, for both DataFrames. - We cannot use
concat()if our DataFrames’ dimensions do not match along the axis in which we are trying to concatenate. - The
concat()has inner (default) and outer joins only, whereasmerge()has left, right, outer, and inner (default) joins.