What is a Java lambda function?
A lambda function is a function declared without a name. Lambda functions have been incorporated in Java 8 to provide preliminary support for functional programming. They are primarily used to implement the abstract function of a functional interface.
Quick reminder: A functional interface is a class with one, and only one, abstract function.
Benefits of using lambda functions include improved readability and less boilerplate code.
Syntax
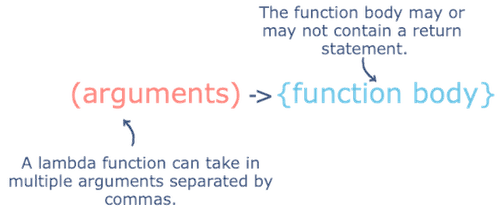
- There can be zero or more arguments. If there is more than one argument, then they need to be enclosed inside the parenthesis.
- If the function body consists of only one line, then curly braces are optional.
- The function body may or may not contain a return statement.
Examples
The example below goes over the basic syntax again.
//convert to upper case and print elements of a listimport java.util.*;class HelloWorld {public static void main( String args[] ) {List <String> myString = new ArrayList<>();myString.add("Hello");myString.add("World");//using a lambda function inside the forEachmyString.forEach(word -> System.out.println(word.toUpperCase()));}}
A functional interface will be used in the following examples to demonstrate how the usage of lambda functions result in cleaner code.
1. Traditional use
// Printing the name of the person along with Hellointerface Hello {void with_name(String Name);}class HelloWorld {public static void main(String args[]) {String name = "Bob";Hello obj = new Hello() {public void with_name(String Name){System.out.println("Hello " + Name);}};obj.with_name(name);}}
2. Using a lambda function
Using explicit argument types
Here we have explicitly mentioned that the Name would be a string:
interface Hello {void with_name(String Name);}class HelloWorld {public static void main(String args[]) {String name= "Bob";Hello obj = (String Name) ->System.out.println("Hello " + Name);obj.with_name(name);}}
Using implicit argument types
Here compiler would infer from the method declaration that the Name would be a string:
interface Hello {void with_name(String Name);}class HelloWorld {public static void main(String args[]) {String name= "Bob";Hello obj = (Name) ->System.out.println("Hello " + Name);obj.with_name(name);}}
Free Resources