What is a starvation problem in an operating system?
Starvation happens if a method is indefinitely delayed. This can emerge once a method needs a further resource for execution that isn’t assigned.
These resources are things like:
- CPU time
- memory
- disk space
- network bandwidth
- I/O access to network or disk
Starvation is the problem that occurs when low priority processes get jammed for an unspecified time as the high priority processes keep executing.
A steady stream of higher-priority methods will stop a low-priority process from ever obtaining the processor.
Measures to handle starvation
-
The resource allocation will be taken by a freelance manager to ensure even distribution.
-
Random choice of processes for resource allocation or processor allocation ought to be avoided as they encourage starvation.
-
The criteria for priority of resource allocation ought to take into account factors like
aging when the priority of a method is hyperbolic it waits longer
Differences between Starvation and Deadlock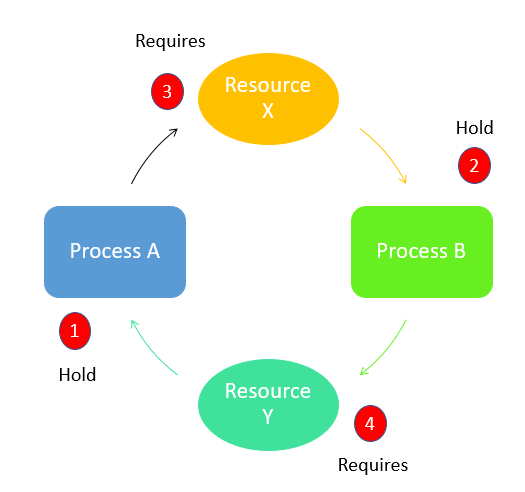
| Starvation | Deadlock |
|---|---|
| 1. It is called lived stock. | 1. It is called circular waiting. |
| 2. Starvation occurs when a process requires a resource for execution that it is never allowed. | 2. A deadlock occurs when two or more processes need some resource to complete the execution held by the other process. |
| 3. Starvation is more of a scheduler issue. | 3. Deadlock is more of a process design/distributed design issue. |