What is Joint Application Development (JAD)?
Overview
Joint Application Development is mainly used to elicit, design, and develop software requirements. This methodology consists of holding a series of collaborative meetings called JAD sessions, ranging from a few hours to many weeks.
Participants of JAD
The term joint in JAD refers to the involvement of multiple stakeholders in the process. Some of the typical participants of the JAD sessions are listed below:
Executive sponsor
These stakeholders are the owners of the system being developed. The perks of this position are that the power to make essential decisions rests in their hands. Moreover, an executive sponsor also provides plans to be followed and implements strategies.
Domain expert
Also referred to as the backbone of a JAD meeting, domain experts are people with exceptional knowledge regarding the system’s domain. Without domain experts and their expertise, a JAD session is considered incomplete since their input is vital for any changes or updates required. A domain expert can be a business user or can also be hired as a third party.
Facilitator
The JAD sessions are handled by facilitators who keep the discussion focused and on track. A facilitator can be referred to as a presiding authority. They do not contribute any information to the JAD session. However, a facilitator serves by bridging the communication barrier between different stakeholders by driving the workshops and sessions.
Documentation expert
A documentation expert plays a vital part in JAD. Without proper documentation, a JAD meeting can be considered incomplete since a JAD document contains the necessary information for software development. A JAD document typically contains essential points of discussions between stakeholders and the agreements reached.
Usage of JAD
JAD is recommended for projects that involve:
- Groups of varying stakeholders representing different departments.
- Stakeholders who are willing to come to sessions and participate in them.
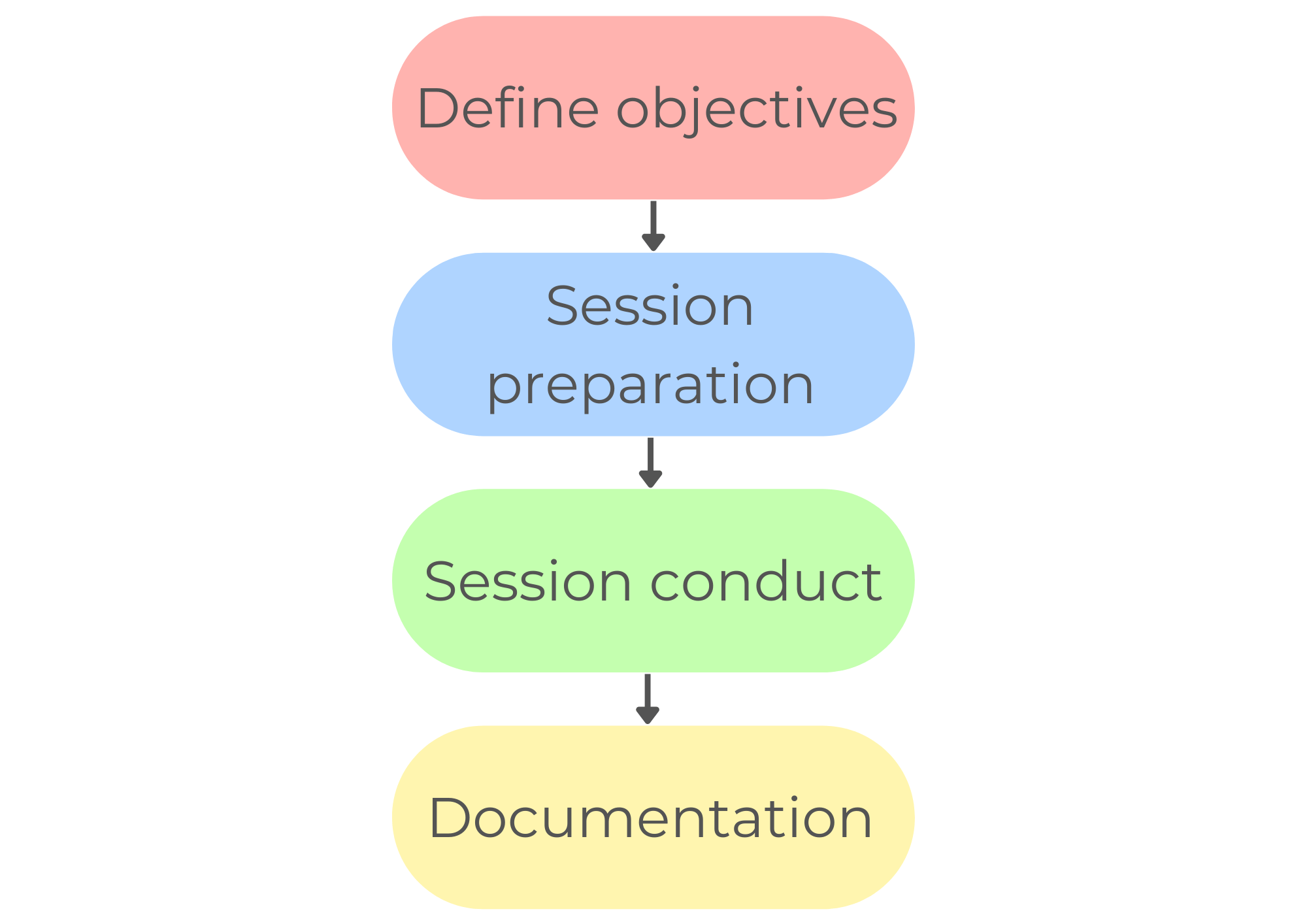
Phases Of JAD
The generic phases of the JAD life cycle include:
1. Define objectives
In this phase, the facilitator articulates the meeting agenda and outcomes and shares them with the participants for review.
2. Session preparation
This phase involves the facilitator researching the session objectives to get a holistic insight and prepare the session’s logistics.
3. Session conduct
The JAD session is conducted in this phase, and the progress is reviewed. Prototypes can be presented in the sessions to resolve conflicts among the stakeholders.
4. Documentation
In this phase, the requirements or design documents are compiled and reviewed.
Benefits of JAD
In JAD, the customer and end-user are involved throughout the development process. This involvement helps to reach a consensus between different groups of stakeholders involved. It also makes it easier to develop solutions for various problems because the customer and IT representatives jointly discuss requirements in detail and agree upon them during the sessions. Therefore, JAD ensures higher customer satisfaction which reduces development time and cost.
Drawbacks of JAD
Since there are varying stakeholders involved in JAD, conflicts are inevitable, and it often takes multiple JAD meetings to reach an agreement. Moreover, JAD sessions demand significant time from all stakeholders, which can be difficult.