What is pooling?
CNN contains many hidden layers for feature extraction and manipulation – here, we are going to discuss pooling in detail.
Why pooling layers?
Pooling layers use different filters to identify different parts of images like edges or corners.
-
The pooling layer operates on each feature map separately to create a new set of the same number of pooled feature maps.
-
The size of the pooling operation or filter is smaller than the size of the feature map.
-
Pooling is a downsampling operation that reduces the dimensionality of the feature map.
-
Its function is to progressively reduce the spatial size of the representation to reduce the number of parameters and computation in the network.
-
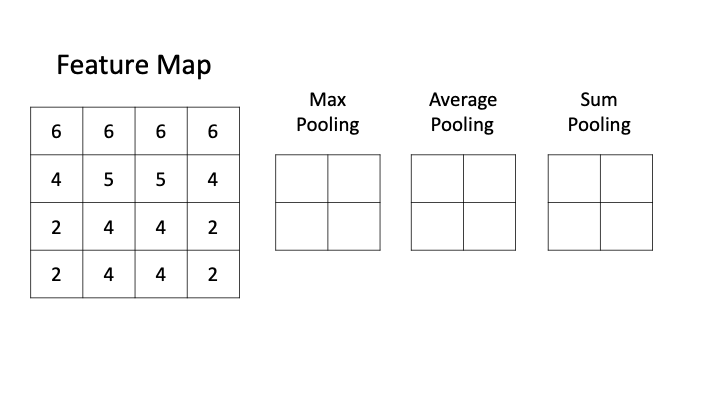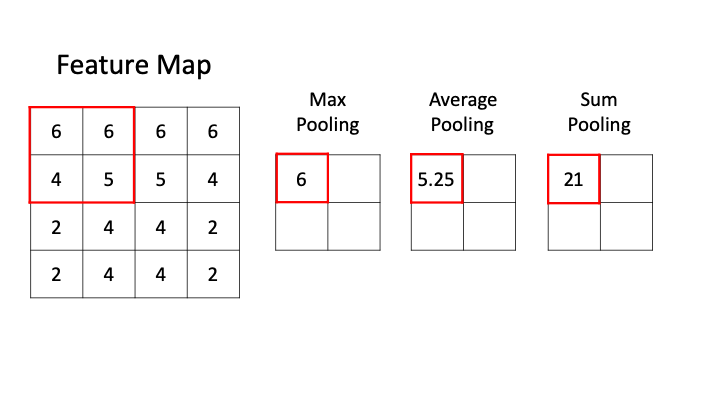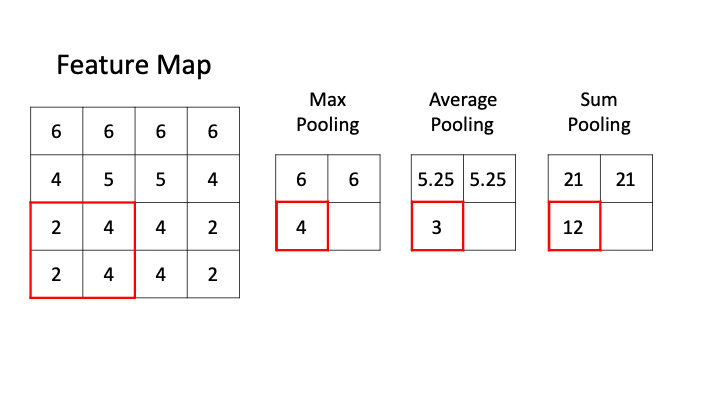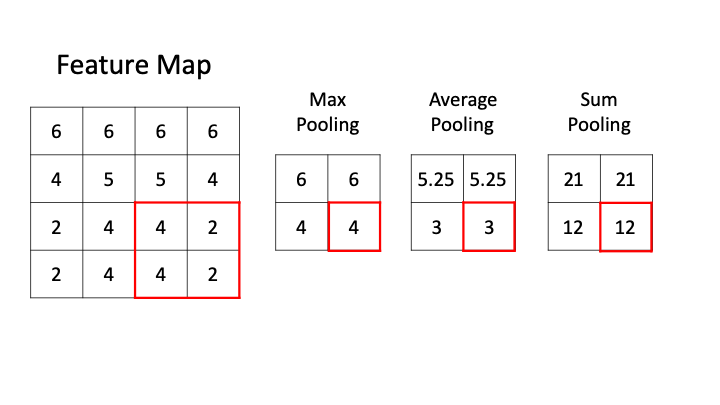
The pooling layer often uses the Max operation to perform the down sampling process.
-
Pooling layers can be further classified as:
-
Max pooling -
Min pooling -
Average pooling -
Sum pooling
Take a look at the code snippet below to better understand max pooling.
import numpy as npfrom keras.models import Sequentialfrom keras.layers import MaxPooling2D#Defining input imageimage=np.array([[4,4,5,7],[10,5,6,3],[8,5,2,4],[3,1,2,6]])image=image.reshape(1,4,4,1)#defining modelusing maxpoolmodel=Sequential([MaxPooling2D(pool_size=2,strides=2)])#generating pooled outputoutput=model.predict(image)#Printing output imageoutput=np.squeeze(output)print(output)