What is the random.gauss() method in Python?
Overview
The gauss method is used to get a floating value chosen from a Gaussian or normal distribution with the given mean and standard deviation.
What is Gaussian or normal distribution?
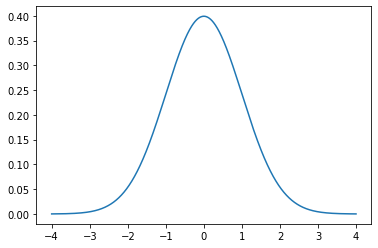
The Gaussian distribution, also known as the normal distribution, is a symmetric probability distribution centered on the mean, indicating that data near the mean occur more frequently than data far from it. The normal distribution will appear as a bell curve on a graph. The following image shows what a bell curve looks like when plotted on a graph.
Syntax
random.gauss(mu, sigma)
Parameters
mu: The mean value.sigma: The standard deviation value.
Return value
This method returns a floating-point value.
Code
Let's look at the code below:
import randommu = 5sigma = 3.4val = random.gauss(mu, sigma=sigma)print("random.gauss(%s, %s) = %s" % (mu, sigma, val))
Code explanation
- Line 1: We import the
randommodule. - Line 3: We define the mean value
mu. - Line 4: We define the standard deviation value
sigma. - Line 5: We store the value returned by
gauss(mu,sigma)in the variableval. - Line 7: We print
valto the console.