What is the traceroute/tracert command and how is it used?
What is tracert/traceroute?
The tracert command (in Windows) or traceroute command (in Linux or Mac) is a network analysis tool that can be used to know the path a
The time duration for this transfer to happen is also recorded with the
When to use the traceroute command
The tracerroute command allows you to:
- Track the path followed or nodes met by your packet en-route to its destination.
- Analyze the different paths in your local network to determine the fastest path following the shortest path protocol.
The routes followed by a packet could be tracked with the traceroute command in real-time using the IP addresses of the different
Result of traceroute command
The traceroute command returns the number of hops encountered by the packet on its way to its destination. The tracert command will also return the IP addresses of all the
Although many routers on the internet today are set to block the
tracertmessages automatically, the result of the command is inaccurate most of the time.
Advantages of tracert
-
It can determine the cause of a response delay in a network.
-
It determines the routing loops present in a network pathway across nodes that send and receive packets.
-
It finds the location of failed points in the network while packets move from source to destination.
Meaning of the tracert command result
Let’s explore what the returned result of a tracert command means. To do this, we head straight to our command prompt or terminal.
Let’s create a traceroute to educative.io. We do this by entering the following command in our terminal or command prompt:
For windows:
tracert www.educative.io
For Linux/Mac:
traceroute www. educative.io
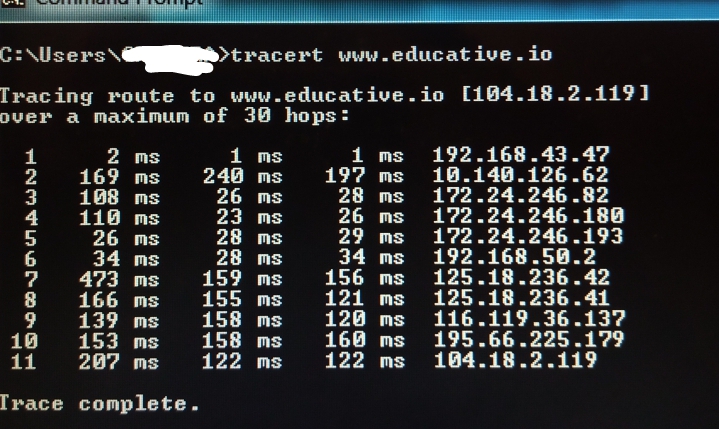
Output
The output might look like the diagram below:
Understanding the output from traceroute
From the example above, the result appears to have five columns.
Columns
-
The first column from the left represents the serial number of the hop count.
-
The second, third, and fourth columns are the time it took for the traditional three
packets network messages tracertcommand to reach a hop. -
The last column represents the IP addresses of all hops encountered.
Rows
-
The rows each represent information about individual hops.
-
The first row
1is the address of the device. It connects the network from which this command was made to the internet. This is called the network internet gateway. -
The second row
2is usually the address of the router from which theISP Internet Service Provider -
Rows
3-9are all hops of other networks, some global networks, and other third-party internet business organizations. Some still belong to your ISP. -
Usually, the one before the last, in this case
10, is the hop address of the network the device is hosting. Therefore, www.educative.io can be located. -
The last row
11is the IP of the device (server) hosting the website educative.io.
Some useful tips
For a compelling diagnosis of your network, try to combine the tracert command with the ping command to get the best results.
Example
-
Suppose you have problems with
timeoutorunreachable errormessages for a site you hosted. -
Before running to your ISP or the hosting company to make complaints, you can run some basic checks with the
tracertand then thepingcommands to discover what the problem is.
Note: You can also use it to know where the network delays are and which path is faulty in your local network. You can start diagnosis from there. Type the command
tracert, without any address, in the command prompt, and you will view the differenttracertoptions which can help you refine yourtracertoutput.