Overview of YAML syntax
Master the fundamental syntax rules of YAML. Learn how to structure data with indentation, key-value pairs, and lists.
In this chapter, you will learn the basic syntax of YAML.
YAML relies on three core elements:
Indentation to show structure
Key-value pairs to store data
Lists to group items
Let’s explore each of these.
Indentation
YAML structures are defined by whitespaces and indentation, similar to those used in the Python programming language. Spaces are the only way to achieve indentation.
YAML uses whitespaces to show relationships between data. Items at the same indentation level are siblings, while indented items are children of the line above them.
Example
parent:
child1: value1
child2: value2
grandchild: value3
Rules
- Use spaces only (2 or 4 spaces per level is standard convention).
- Please ensure consistency by choosing either 2 or 4 spaces and maintaining that choice throughout the entire document.
- Do not use tabs; tabs are NOT allowed in YAML.
Tip: Enable "Show Whitespace" in your text editor to catch tab characters.
Representing data in YAML
YAML is used to store lists (sequences) of elements and key-value pairs (mappings).
A list (also known as a sequence) is an ordered collection of items. Each item within the sequence is separated by a new line followed by a comma (
,) character. An item can be of any type, like strings, numbers, or maps.Key-value pairs (also known as mappings) are unordered collections of key-value pairs. But the keys are not unique because they can contain duplicate values. A newline followed by a colon separates each element in a mapping (
:).
Key-value pairs
A key-value pair is a data structure consisting of a key and a value. The key identifies the value, which can be of any data type.
Key-value pairs are represented using the following syntax:
<key>: <value>
Rules
- The colon (
:) separates the key from the value. - A space after the colon is mandatory.
Key-value pair example:
key: value
The following is the graphical representation of the key value pair:
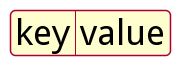
Lists (Sequences)
A list (or sequence) is a simple data structure consisting of zero or more ordered items. In other words, a list is an ordered collection of data.
A list is represented by preceding its items with - (hyphen).
Syntax
- <element 1>
- <element 2>
- ...
- <element n>
Rules
Each item starts with a hyphen (
-) followed by a spaceItems can be any type: strings, numbers, or even nested structures
The following is the graphical representation of the list:

Simple, yet powerful
YAML’s simple syntax does not limit its language capabilities. The language is rich enough to represent almost any conceivable data structure or object inside a running computer program as a readable plain text file.
Below are some of the key features of YAML that make it an excellent option for data formatting.
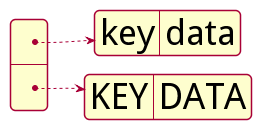
Case Sensitivity
YAML is case sensitive, so the key “DATA” would be different from “data”.
Each of the items in the list below will be treated as a unique list item and a unique key/value pair as the string contains different cases of alphabets.
The following is the graphical representation of the sample YAML data in the code example above:

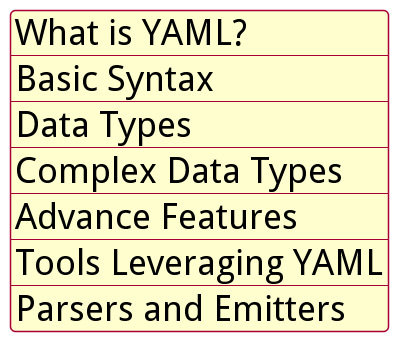
Below is a list of learning objectives of this course.
The code below represents the above list in the form of YAML.
The following is the graphical representation of the YAML data representing learning objectives for this course:
In a C-based programming language, this would have been represented programmatically as the code snippet below:
LearningObjectives[0] = "What is YAML?"
LearningObjectives[1] = "Basic Syntax"
LearningObjectives[2] = "Data Types"
LearningObjectives[3] = "Complex Data Types"
LearningObjectives[4] = "Advance Features"
LearningObjectives[5] = "Tools Leveraging YAML"
LearningObjectives[6] = "Parsers and Emitters"
It should now be clear to you from the example above that YAML has a very simple data format.
Multi-Document support in YAML
To define a YAML file, we mostly use either .yml or .yaml extensions, for example, config.yml. However, some tools may use a different extension to specify the purpose of the file.
Examine the code snippet below to learn how to create multiple documents within a single file or stream.
---
- XML
- JSON
- CSV
---
- Unicode
- ASCII
- UTF8
...
Rules
- A YAML stream is a collection of zero or more documents.
- An empty stream contains no documents.
- A single document may or may not be marked with (
---). - You can add multiple documents to a single YAML file.
- Different documents are separated using three dashes (
---). - Most files only contain one document, so
---is often omitted - Documents could end with (
...). - Three dots (
...) are used to mark the end of a document without starting a new one. (optional)
Real-World Use: Kubernetes configurations often use multi-document files to define multiple resources.
Below is the graphical representation of this format.
Block style vs Flow style
YAML supports two writing styles:
Block style
A document in block style uses spaces for structuring the document. It is much easier to read, but it is less compact.
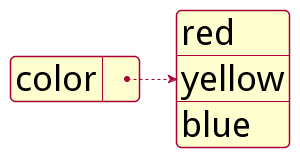
Example
color:
- red
- yellow
- blue
Below is the graphical representation of the data:
Flow style
YAML has an alternate syntax called flow style, it allows sequences and mappings to be written inline without having to rely on indentation, using a pair of square brackets [] and curly brackets {} respectively.
Flow style is an extension of JSON. It is less easy to read; however, it provides more compactness.
Examples
color: [red, blue]
and
- { name: 'James', age: 35 }
When to use each:
Block style: Use it for configuration files and documentation. It prioritizes readability.
Flow style: Use it for short lists or when space is limited.
Best Practice: Use block style unless you have a specific reason not to.
Comments
Any text after # not enclosed in ''(quotes) or "" (double quotes) is considered a comment. It marks the beginning of a comment, and any text until the end of the line is completely ignored. You use this to write notes on the file or temporarily disable some section of the file.
Below are some examples of the comments
Example
## A single line comment
A comment can begin anywhere in the line.
Example
## document starts below
---
key: "value" # mapping
# A list of two items
list:
- "item 1" # first value
- "item 2" # second value
---
## end of document
Tip: YAML does not support block or multi-line comments.
In order to create a multi-line comment, you need to suffix each line with a # character.
Example
## This is a multi-line
## comment in YAML. There is
## no alternate way of creating
## block comments.
Below is another example of YAML comments:
# __ __ __ __ _
# \ \ / / /\ | \/ || |
# \ \_/ / / \ | \ / || |
# \ / / /\ \ | |\/| || |
# | | / ____ \ | | | || |____
# |_|/_/ \_\|_| |_||______|
Summary
- Items of a list in YAML are represented by preceding it with
-(hyphen). - Key value pairs in YAML are represented as
<key>:<value>. - YAML is case sensitive.
- YAML uses spaces and indentations to define document structure.
- To define a YAML file we use either .yml or .yaml as file extension.
- Different documents in YAML can be separated using three dashes (
---). - You use three dots (
...) to mark the end of a document without starting a new one. - A document in block style uses spaces to structure the document.
- Flow style makes YAML an extension of JSON. Flow style is a little less human-readable than block style, however it provides more compactness to the document.
- Any text after
#not enclosed in''(quotes) or""(double quotes) is considered a comment. - YAML does not support block or multi-line comments.
Quiz on Basic YAML Syntax
YAML does not support comments.
True
False