What is data flow form in Angular 8?
Overview
For valuable application creation in Angular, it is essential to have knowledge of how the framework handles data flow.
The MVC architecture
Angular makes use of model view controller (MVC) architecture for its web application development.
-
The model part in MVC of the architecture manages the application data.
-
The view part manages the data display to the users.
-
The controller handles the interaction between the view and the model end.
Types of Angular forms
The data flow occurrence is between the view and the model end of the architecture. This can be explained through various form types in Angular as seen below.
-
FormControl: AnAngularclass that sets and gets validation and values for the form control field. -
SetValue(): A method inAngularFormGroup that helps set the value of a control in a FormGroup. -
ValueChanges: This is an event raised byAngularform whenever the value of the form control group is changed. -
Ngmodelchange: An event inAngularthat helps us gain user input when we listen. -
NgControlgroup: Use to bind a control group to aDOM. -
ngmodel: An inbuilt directive inAngularthat helps create a form control instance. -
DOM: The document object model is a programming interface of web documents.
Angular form types approaches
Angular form types are characterized in two approaches:
- Template-driven.
- Reactive.
These two approaches are illustrated below.
-
viewtomodelflow, i.e., data parsed from the view end to the model end. -
the
modeltoviewflow, i.e., data being parsed from the model end to the view end ofangulararchitecture.
1. Template Driven Approach
The template-driven approach is the most straightforward form creation approach.
Here forms are generated by the form.value object.
Form data can be exported as a
JSONobject when a submit method is triggered.
We can use the ngModel to add controls to a form, while the ngControlGroup module groups multiple controls.
Regarding the flow of data, individual form elements are linked to directives that help to internally manage the form model.
View to model data flow steps for the template-driven approach
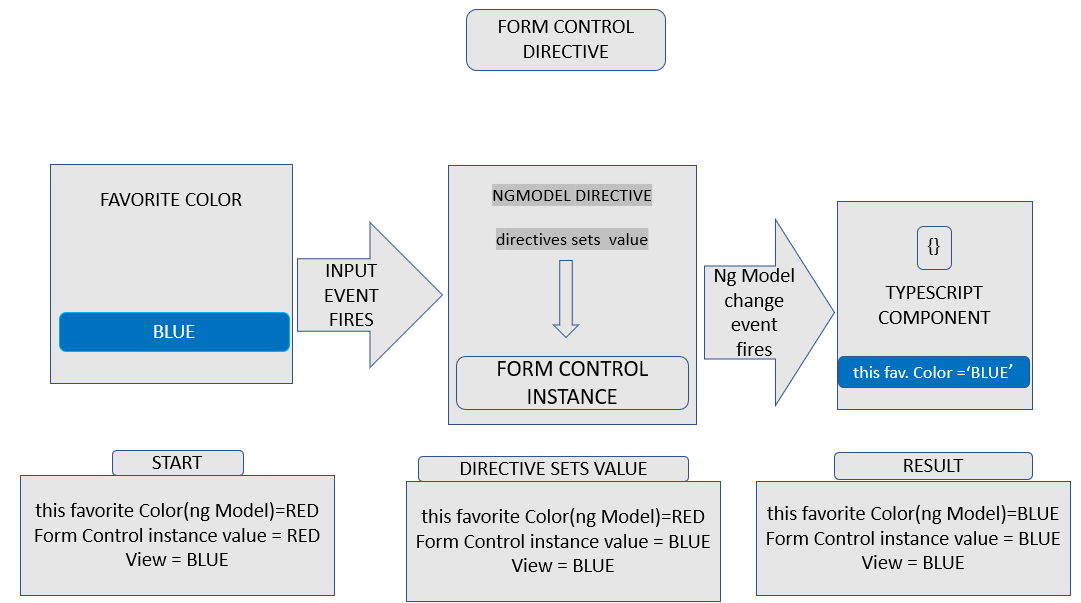
Step 1. The user initiates action by entering a value into the input element, say, blue.
Step 2. An input event with the latest value, which is blue, is displayed by the input element.
Step 3. From the FormControl instance, the setValue() method is initiated by the control value accessor found in the input.
Step 4. The FormControl instance through the valueChanges observables outputs the latest value just after the setValue() method, and the latest value is received by the subscriber to the valueChanges observable.
Step 5. The NgModel.viewToModelUpdae() method is now triggered by the control value accessor. It outputs an ngModelChange event.
Step 6. Finally, the latest value, which is blue, is on output by the ngModelChange event, and it is used to update the defined property in the component. The component template here makes use of two-way data binding.
Model to view data flow steps for the template-driven approach
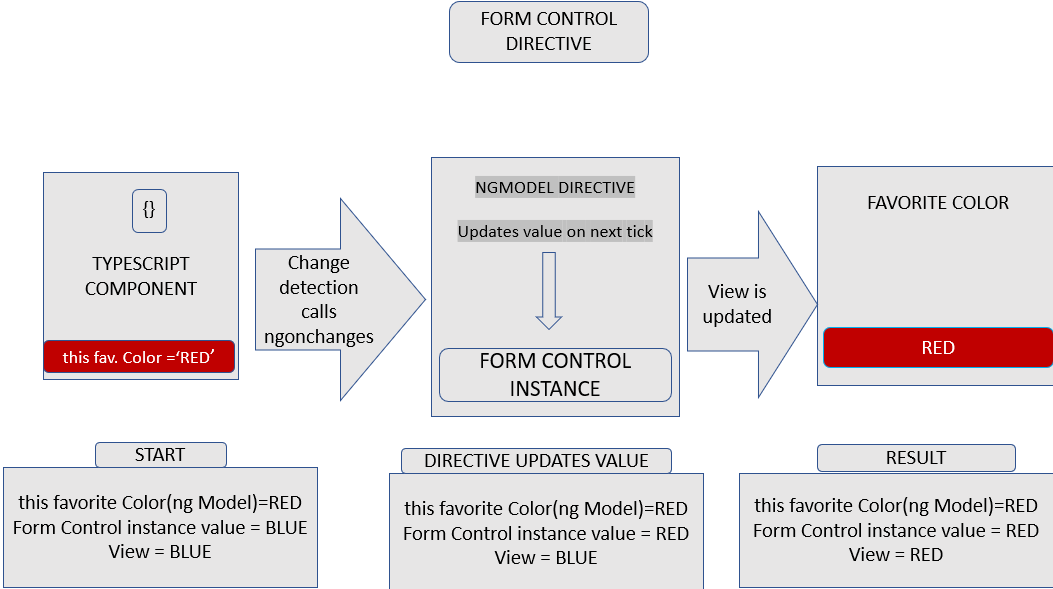
Step 1. Here, the defined property gets updated to a new value in the component.
Step 2. The change detection can begin at this point.
Step 3. The ngOnChange lifecycle hook is triggered on the Ngmodel directive instance during the change detection. This is because there is a change in one of its inputs.
Step 4. An async task is queued by the ngOnChanges() method, this sets the value of the internal FormControl instance.
Step 5. The change detection can now be termed complete at this point.
Step 6. Execution is carried out on the necessary task in other to set the FormControl instance value.
Step 7. The FormControl instance through the valueChanges observable outputs the latest value.
Step 8. The latest value is received by the subscriber to the valueChanges observable.
Step 9. The form input element in the view part of the architecture is updated by the control value accessor with the latest value of the property.
2. Reactive Form Data Flow
Data flow here is synchronous from the view to the model and the model to the view part of the angular architecture.
There is no reliance on the view aspect of the architecture, and the reactive approach works in a code-driven manner.
We have the steps for the data flow below.
View to model data flow steps for the reactive approach
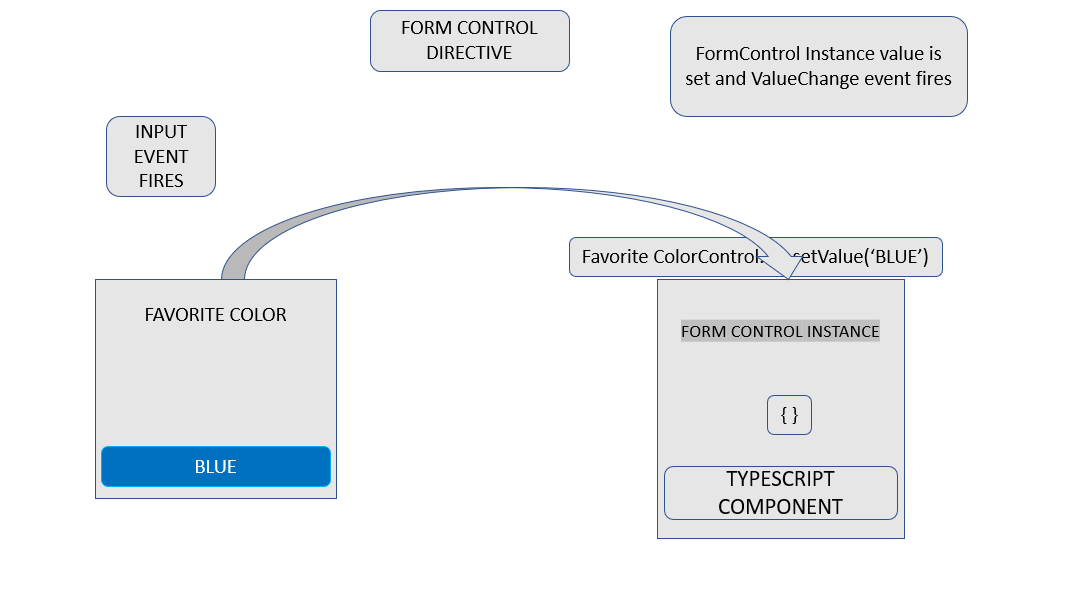
Step 1. The user initiates action by typing a value in the input element.
Step 2. The form input element now outputs the latest input value.
Step 3. After listening for events on the form input, the control value accessor relays the latest value input to the FormControl instance.
Step 4. The FormControl instance can now output the latest value through valueChanges observables.
Step 5. Any subscriber on the valueChanges observable receives the new value.
Model to view data flow steps for the reactive approach
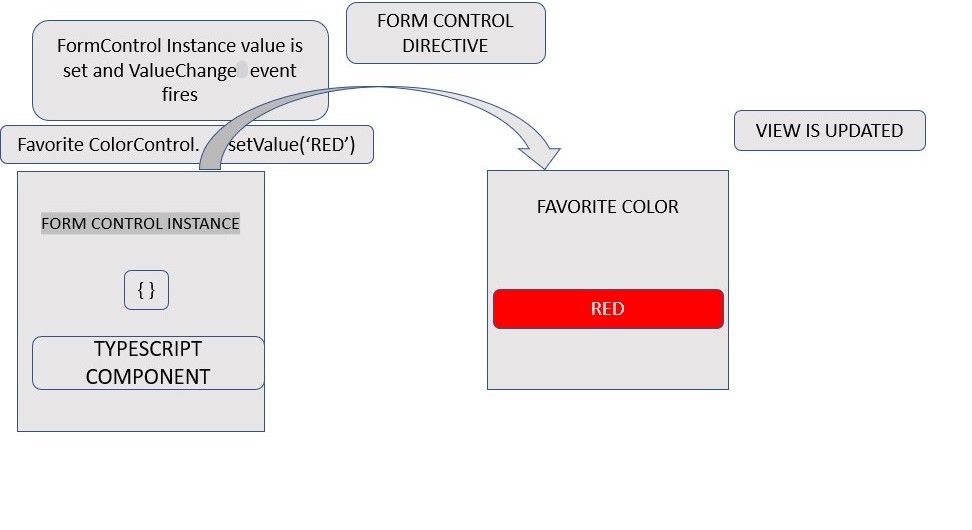
Step 1. The user initiates a call to update the formControl value.
Step 2. The FormControl instance outputs the latest value through the valueChanges observable.
Step 3. The latest value is now received by the subscriber through valueChanges observables.
Step 4. The control value accessor updates the element with the latest value on the form input element.