Benefits of using cluster computing
Learn about the benefits of cluster computing in high-performance computing systems. Understand how parallelism enables concurrent processing across many tasks, the types of problems suited for HPC, and the limitations to consider when deciding to use cluster computing.
We'll cover the following...
HPC systems derive their computational power by exploiting parallelism. Programs for HPC systems must be splitted up into many smaller sub-programs which can be executed in parallel on different processors. HPC systems can offer parallelism at a much larger scale, with 100’s or 1000’s, or even millions of tasks running concurrently.However, writing parallel software can be challenging, and many existing software packages do not already support parallelism & may require development.
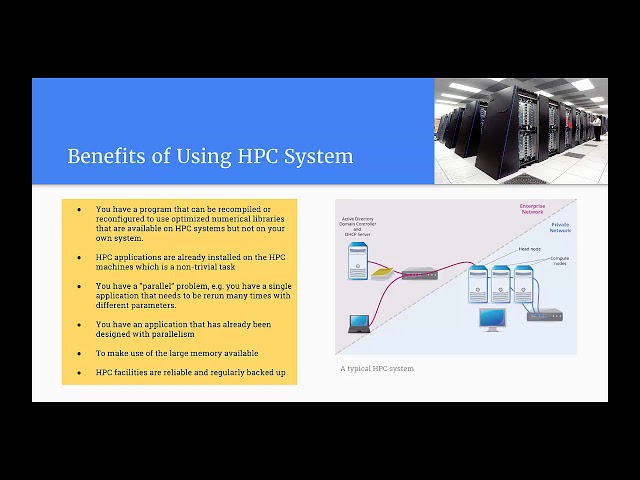
Therefore, HPCs are userful when you have:
-
A program that can be recompiled or reconfigured to use optimized numerical libraries that are available on HPC systems but not on your own system;
-
You have a parallel problem, e.g. you have a single application that needs to be rerun many times with different parameters;
-
You have an application that has already been designed with parallelism;
-
To make use of the large memory available;
-
problem solutions require backups for future use. HPC facilities are reliable and regularly backed up.
When not to use HPC systems?
-
You have a single threaded job which will only run one job at a time (typical of MatLab users);
-
You rely on DBMS/ databases;
-
You have a lot of data to transfer between your local machine and the HPC on a continuous basis (e.g. per job);
-
You need to have a GUI to interact with your program.