Binary Trees in Python
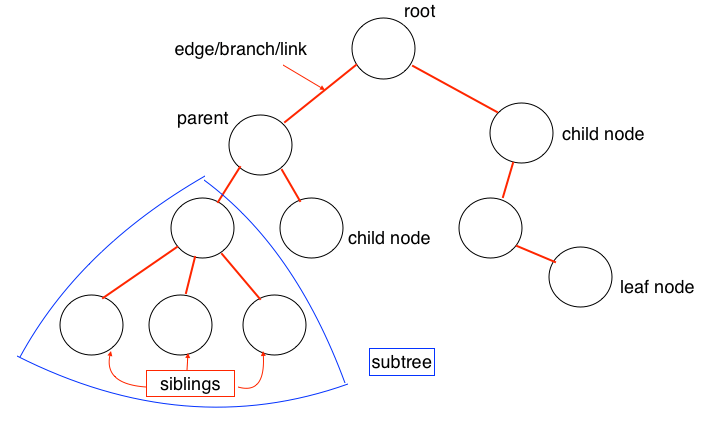
Tree is a non-linear data structure. It is a hierarchical data structure that has nodes connected through links. The topmost node of the tree which has no parent is known as the root node.
Binary Tree
Binary Tree is a form of a tree whose nodes cannot have more than two children. Each node of the binary tree has two pointers associated with it, one points to the left child, and the other points to the right child of the node. It is an unordered tree having no fixed organized structure for the arrangement of nodes.
Note: Binary Tree is slow for the searching, insertion, or deletion of the data because of its unordered structure. The time complexity of these operations is .
Binary Search Tree
Binary Search Tree(BST) is a type of binary tree which is in ordered form. It has a fixed organized structure for the arrangement of nodes. The structure follows the following rules:
- Left child of the node must have a value less than its parent’s value
- Right child of the node must have a value greater than its parent’s value
Note: BST is faster than a binary tree in the searching, insertion, or deletion of the data because of its ordered structure. The time complexity of these operations is .
Implementation
We have created a node class and instantiated the root node with .
# Creating node classclass Node:def __init__(self, data):self.data = dataself.leftChild = Noneself.rightChild = None# print functiondef PrintTree(self):print(self.data)# Creating a root noderoot = Node(27)root.PrintTree()
Insertion
The insert method compares the value with the value of the root node and decides whether to insert it on the left or the right side of the BST.
Remember: If the value is lesser than the value of the parent node, it is inserted on the left side; otherwise, it’s inserted on the right side of the BST.
Finally, the PrintTree method is used to print the BST.
# Creating node classclass Node:def __init__(self, data):self.data = dataself.leftChild = Noneself.rightChild = None# Function to insert in BSTdef insert(self, data):# if value is lesser than the value of the parent nodeif data < self.data:if self.leftChild:# if we still need to move towards the left subtreeself.leftChild.insert(data)else:self.leftChild = Node(data)return# if value is greater than the value of the parent nodeelse:if self.rightChild:# if we still need to move towards the right subtreeself.rightChild.insert(data)else:self.rightChild = Node(data)return# function to print a BSTdef PrintTree(self):if self.leftChild:self.leftChild.PrintTree()print( self.data),if self.rightChild:self.rightChild.PrintTree()# Creating root noderoot = Node(27)# Inserting values in BSTroot.insert(14)root.insert(35)root.insert(31)root.insert(10)root.insert(19)# printing BSTroot.PrintTree()
Searching
The search method compares the value with the value of the root node and if not matched it decides whether to search it on the left or the right side of the BST.
Remember: If the value is lesser than the value of the parent node, it is searched on the left side; otherwise, it’s searched on the right side of the BST.
# Creating node classclass Node:def __init__(self, data):self.data = dataself.leftChild = Noneself.rightChild = None# Function to insert in BSTdef insert(self, data):# if value is lesser than the value of the parent nodeif data < self.data:if self.leftChild:# if we still need to move towards the left subtreeself.leftChild.insert(data)else:self.leftChild = Node(data)return# if value is greater than the value of the parent nodeelse:if self.rightChild:# if we still need to move towards the right subtreeself.rightChild.insert(data)else:self.rightChild = Node(data)return# Function to search in BSTdef search(self, val):# if value to be searched is foundif val==self.data:return str(val)+" is found in the BST"# if value is lesser than the value of the parent nodeelif val < self.data:# if we still need to move towards the left subtreeif self.leftChild:return self.leftChild.search(val)else:return str(val)+" is not found in the BST"# if value is greater than the value of the parent nodeelse:# if we still need to move towards the right subtreeif self.rightChild:return self.rightChild.search(val)else:return str(val)+" is not found in the BST"# function to print a BSTdef PrintTree(self):if self.leftChild:self.leftChild.PrintTree()print( self.data),if self.rightChild:self.rightChild.PrintTree()# Creating root noderoot = Node(27)# Inserting values in BSTroot.insert(14)root.insert(35)root.insert(31)root.insert(10)root.insert(19)# searching the valuesprint(root.search(7))print(root.search(14))
Free Resources