How to use bidirectional search implementation in Python
A graph is a network of nodes connected by arcs or edges.
The two basic graph search algorithms,
A graph search is done in one direction, either from the source/initial vertex to the goal/target vertex.
To search from both ends simultaneously, a bidirectional search is implemented.
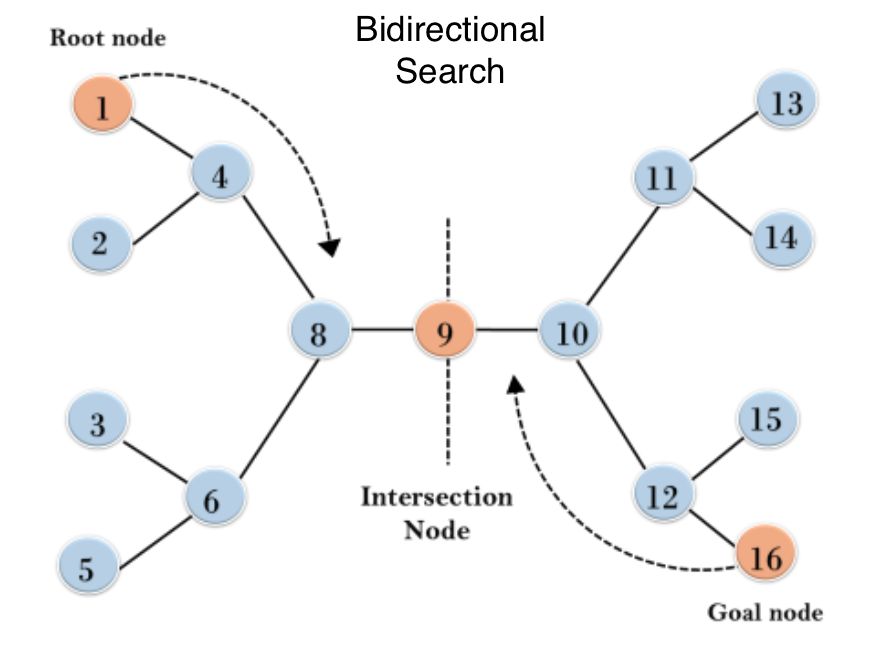
Bidirectional search
Bidirectional search is a graph search algorithm that finds the shortest path from a source vertex to a goal vertex.
In implementing bidirectional search in Python, the graph search can either be:
- Forward search from the source to the goal vertex.
- Backward search from the goal to the source vertex.
The intersection of both forward and backward graphs indicates the end of the search, as displayed below.
Advantages and disadvantages of bidirectional search in Python
| Advantage | Disadvantage |
|---|---|
| 1. Less time consuming as the shortest path length is used for the search. | The goal node has to be known before the search can be done simultaneously in both directions. |
When is it possible to use bidirectional search in Python?
The bidirectional approach can be used:
- When the branching factor for the forward and reverse direction is the same.
- When both the source and goal vertices are specified and distinct from each other.
Bidirectional search implementation in Python
Below is an implementation of bidirectional search in Python using BFS:
class adjacent_Node:def __init__(self, v):self.vertex = vself.next = Noneclass bidirectional_Search:def __init__(self, vertices):self.vertices = verticesself.graph = [None] * self.verticesself.source_queue = list()self.last_node_queue = list()self.source_visited = [False] * self.verticesself.last_node_visited = [False] * self.verticesself.source_parent = [None] * self.verticesself.last_node_parent = [None] * self.verticesdef AddEdge(self, source, last_node):node = adjacent_Node(last_node)node.next = self.graph[source]self.graph[source] = nodenode = adjacent_Node(source)node.next = self.graph[last_node]self.graph[last_node] = nodedef breadth_fs(self, direction = 'forward'):if direction == 'forward':current = self.source_queue.pop(0)connected_node = self.graph[current]while connected_node:vertex = connected_node.vertexif not self.source_visited[vertex]:self.source_queue.append(vertex)self.source_visited[vertex] = Trueself.source_parent[vertex] = currentconnected_node = connected_node.nextelse:current = self.last_node_queue.pop(0)connected_node = self.graph[current]while connected_node:vertex = connected_node.vertexif not self.last_node_visited[vertex]:self.last_node_queue.append(vertex)self.last_node_visited[vertex] = Trueself.last_node_parent[vertex] = currentconnected_node = connected_node.nextdef is_intersecting(self):#for i in range(self.vertices):if (self.source_visited[i] andself.last_node_visited[i]):return ireturn -1def path_st(self, intersecting_node,source, last_node):path = list()path.append(intersecting_node)i = intersecting_nodewhile i != source:path.append(self.source_parent[i])i = self.source_parent[i]path = path[::-1]i = intersecting_nodewhile i != last_node:path.append(self.last_node_parent[i])i = self.last_node_parent[i]print("*****Path*****")path = list(map(str, path))print(' '.join(path))def bidirectional_search(self, source, last_node):self.source_queue.append(source)self.source_visited[source] = Trueself.source_parent[source] = -1self.last_node_queue.append(last_node)self.last_node_visited[last_node] = Trueself.last_node_parent[last_node] = -1while self.source_queue and self.last_node_queue:self.breadth_fs(direction = 'forward')self.breadth_fs(direction = 'backward')intersecting_node = self.is_intersecting()if intersecting_node != -1:print("Path exists between {} and {}".format(source, last_node))print("Intersection at : {}".format(intersecting_node))self.path_st(intersecting_node,source, last_node)exit(0)return -1if __name__ == '__main__':n = 17source = 1last_node = 16my_Graph = bidirectional_Search(n)my_Graph.AddEdge(1, 4)my_Graph.AddEdge(2, 4)my_Graph.AddEdge(3, 6)my_Graph.AddEdge(5, 6)my_Graph.AddEdge(4, 8)my_Graph.AddEdge(6, 8)my_Graph.AddEdge(8, 9)my_Graph.AddEdge(9, 10)my_Graph.AddEdge(10, 11)my_Graph.AddEdge(11, 13)my_Graph.AddEdge(11, 14)my_Graph.AddEdge(10, 12)my_Graph.AddEdge(12, 15)my_Graph.AddEdge(12, 16)out = my_Graph.bidirectional_search(source, last_node)if out == -1:print("No path between {} and {}".format(source, last_node))