Table of Contents
Delete Node with a Given Key
Problem Statement#
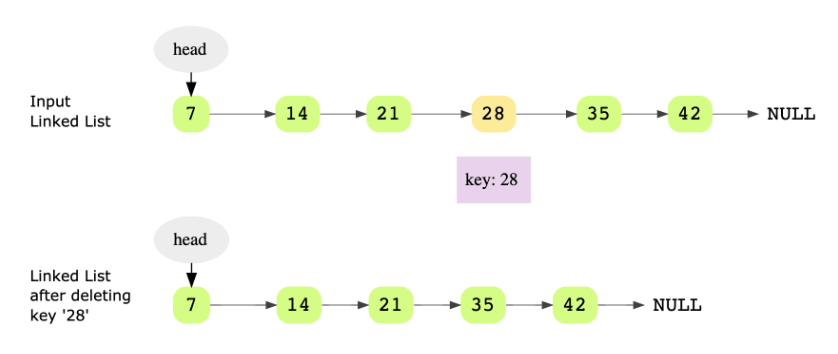
We are given the head of a linked list and a key. We have to delete the node that contains this given key. The following two examples elaborate on this problem further.
Solution#
Solution Explanation#
Runtime Complexity#
Linear, O(n)
Memory Complexity#
Constant, O(1)
Solution Breakdown#
First, we have to find the key in the linked list. We’ll keep two pointers, current and previous, as we iterate the linked list.
If the key is found in the linked list, then the current pointer would be pointing to the node containing the key to be deleted. The previous should be pointing to the node before the key node.
This can be done in a linear scan and we can simply update current and previous pointers as we iterate through the linked list.
Practice problems like this and many more by checking out our Grokking the Coding Interview: Patterns for Coding Questions course!