Copy Linked List with Arbitrary Pointer
Problem Statement
You are given a linked list where the node has two pointers. The first is the regular next pointer. The second pointer is called arbitrary_pointer and it can point to any node in the linked list. Your job is to write code to make a deep copy of the given linked list. Here, deep copy means that any operations on the original list (inserting, modifying and removing) should not affect the copied list.
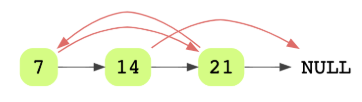
Here’s an example of a linked list with arbitrary pointers connected.
Hint
- Hash table
Try it yourself
LinkedListNode* deep_copy_arbitrary_pointer(LinkedListNode* head) {//TODO: Write - Your - Codereturn NULL;}
Solution
LinkedListNode* deep_copy_arbitrary_pointer(LinkedListNode* head) {if (head == nullptr) {return nullptr;}LinkedListNode* current = head;LinkedListNode* new_head = nullptr;LinkedListNode* new_prev = nullptr;unordered_map<LinkedListNode*, LinkedListNode*> map;// create copy of the linked list, recording the corresponding// nodes in hashmap without updating arbitrary pointerwhile (current != nullptr) {LinkedListNode* new_node =new LinkedListNode(current->data);// copy the old arbitrary pointer in the new nodenew_node->arbitrary_pointer = current->arbitrary_pointer;if (new_prev != nullptr) {new_prev->next = new_node;}else {new_head = new_node;}map[current] = new_node;new_prev = new_node;current = current->next;}LinkedListNode* new_current = new_head;// updating arbitrary_pointerwhile (new_current != nullptr) {if (new_current->arbitrary_pointer != nullptr) {LinkedListNode* node =map[new_current->arbitrary_pointer];new_current->arbitrary_pointer = node;}new_current = new_current->next;}return new_head;}LinkedListNode* create_linked_list_with_arb_pointers(int length) {LinkedListNode* head = LinkedList::create_random_list(length);vector<LinkedListNode*> v;LinkedListNode* temp = head;while (temp) {v.push_back(temp);temp = temp->next;}for (size_t i = 0; i < v.size(); ++i) {int j = rand() % v.size();int p = rand() % 100;if ( p < 75) {v[i]->arbitrary_pointer = v[j];}}return head;}void print_with_arb_pointers(LinkedListNode* head) {while (head != nullptr) {cout << head->data << " (";if (head->arbitrary_pointer)cout << head->arbitrary_pointer->data;cout << "), ";head = head->next;}cout << endl;}// Test Program.int main() {LinkedListNode* head = create_linked_list_with_arb_pointers(15);print_with_arb_pointers(head);LinkedListNode* head2 = deep_copy_arbitrary_pointer(head);print_with_arb_pointers(head2);return 0;}
Solution Explanation
Runtime Complexity
Linear, O(n).
Memory Complexity
Linear, O(n).
Solution Breakdown
This approach uses a map to track arbitrary nodes pointed by the original list. You will create a deep copy of the original linked list (say list_orig) in two passes.
- In the first pass, create a copy of the original linked list. While creating this copy, use the same values for data and
arbitrary_pointerin the new list. Also, keep updating the map with entries where the key is the address to the old node and the value is the address of the new node. - Once the copy has been created, do another pass on the copied linked list and update arbitrary pointers to the new address using the map created in the first pass.
Practice problems like this and many more by checking out our Grokking the Coding Interview: Patterns for Coding Questions course!