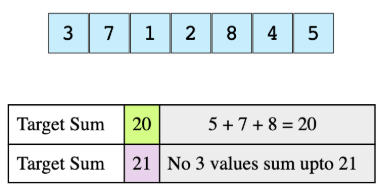
Sum of Three Values
Problem Statement
Given an array of integers and a value, determine if there are any three integers in the array whose sum equals the given value.
Consider this array and the target sums.
Hint
- Sort data
- Iterate from both ends
Try it yourself
bool find_sum_of_three(vector<int> arr,int required_sum) {// TODO: Write - Your - Codereturn false;}
Solution
bool find_sum_of_two(vector<int>& A, int val,size_t start_index) {for (int i = start_index, j = A.size() - 1; i < j;) {int sum = A[i] + A[j];if (sum == val) {return true;}if (sum < val) {++i;} else {--j;}}return false;}bool find_sum_of_three_v3(vector<int> arr,int required_sum) {std::sort(arr.begin(), arr.end());for (int i = 0; i < arr.size() - 2; ++i) {int remaining_sum = required_sum - arr[i];if (find_sum_of_two(arr, remaining_sum, i + 1)) {return true;}}return false;}int main(){vector<int> arr = {-25, -10, -7, -3, 2, 4, 8, 10};cout<<"-8: " <<find_sum_of_three_v3(arr, -8)<<endl;cout<<"-25: "<<find_sum_of_three_v3(arr, -25)<<endl;cout<<"0: " <<find_sum_of_three_v3(arr, 0)<<endl;cout<<"-42: " <<find_sum_of_three_v3(arr, -42)<<endl;cout<<"22: " <<find_sum_of_three_v3(arr, 22)<<endl;cout<<"-7: " <<find_sum_of_three_v3(arr, -7)<<endl;cout<<"-3: " <<find_sum_of_three_v3(arr, -3)<<endl;cout<<"2: " <<find_sum_of_three_v3(arr, 2)<<endl;cout<<"4: " <<find_sum_of_three_v3(arr, 4)<<endl;cout<<"8: " <<find_sum_of_three_v3(arr, 8)<<endl;cout<<"7: " <<find_sum_of_three_v3(arr, 7)<<endl;cout<<"1: " <<find_sum_of_three_v3(arr, 1)<<endl;return 0;}
Solution Explanation
Runtime Complexity
Quadratic, O(n2)
Memory Complexity
Constant, O(1)
Solution Breakdown
In this solution, we first sort the array. Then we fix one element ‘e’, and try to find a pair (a, b) in the remaining array such that required_sum - e = a + b.
We start with the first element e in the array (at index i = 0) and try to find such a pair (a, b) in the remaining array (i.e A[i + 1] to A[n - 1]) that satisfies the condition: a+b = required_sum - e. We can find such a pair in linear time. If we find such a pair, we have found the solution: a, b and e and thus, we can stop the iteration.
Otherwise, we repeat the above steps for all elements e at index i = 1 to n - 3, until we find a pair that meets the condition.
Practice problems like this and many more by checking out our Grokking the Coding Interview: Patterns for Coding Questions course!