React is one of the most widely used libraries for building fast, interactive user interfaces. Whether you’re creating small components or full-scale applications, React 19 provides tools that help you build reliable, maintainable, and modern frontend experiences.
In this course, you’ll start with the fundamentals: how components work, how state drives changes in the UI, and how interactions shape the user experience. Next, you’ll explore more advanced concepts such as managing growing state needs, structuring clean and predictable forms, working with server data, and applying modern React 19 features that keep your interface responsive as your application becomes more complex.
By the end of the course, you’ll be able to build thoughtful, data-driven interfaces with confidence. You’ll have the skills to design components, manage asynchronous data, and structure real-world application logic with the help of a guided Capstone project.
React is one of the most widely used libraries for building fast, interactive user interfaces. Whether you’re creating small com...Show More
WHAT YOU'LL LEARN
An understanding of how React 19 builds dynamic, component-based user interfaces
A working knowledge of managing state in both simple and increasingly complex applications
Hands-on experience creating predictable, well-structured forms with validation and feedback
Familiarity with handling server data, including loading states, error handling, and data refreshing
The ability to apply modern React 19 features that keep UIs fast and responsive as applications scale
Practical experience building a complete web application through a guided Capstone Project
An understanding of how React 19 builds dynamic, component-based user interfaces
Show more
Learning Roadmap
YOUR ROADMAP
2.
JavaScript for React—A Quick Refresher
JavaScript for React—A Quick Refresher
Revise JavaScript fundamentals, modern ES6+ features, and DOM essentials to build a strong foundation for React development in this chapter.
Variables and Data TypesFunctions, Arrow Functions, and CallbacksScope and ClosuresObjects and ArraysJavaScript Asynchronous ProgrammingModern JavaScript and ES6+ FeaturesDOM Essentials for React DevelopersQuiz: JavaScript Fundamentals for ReactChallenge: Dynamic To-Do List ApplicationSolution: Dynamic To-Do List Application
3.
Introduction to React
Introduction to React
8 Lessons
8 Lessons
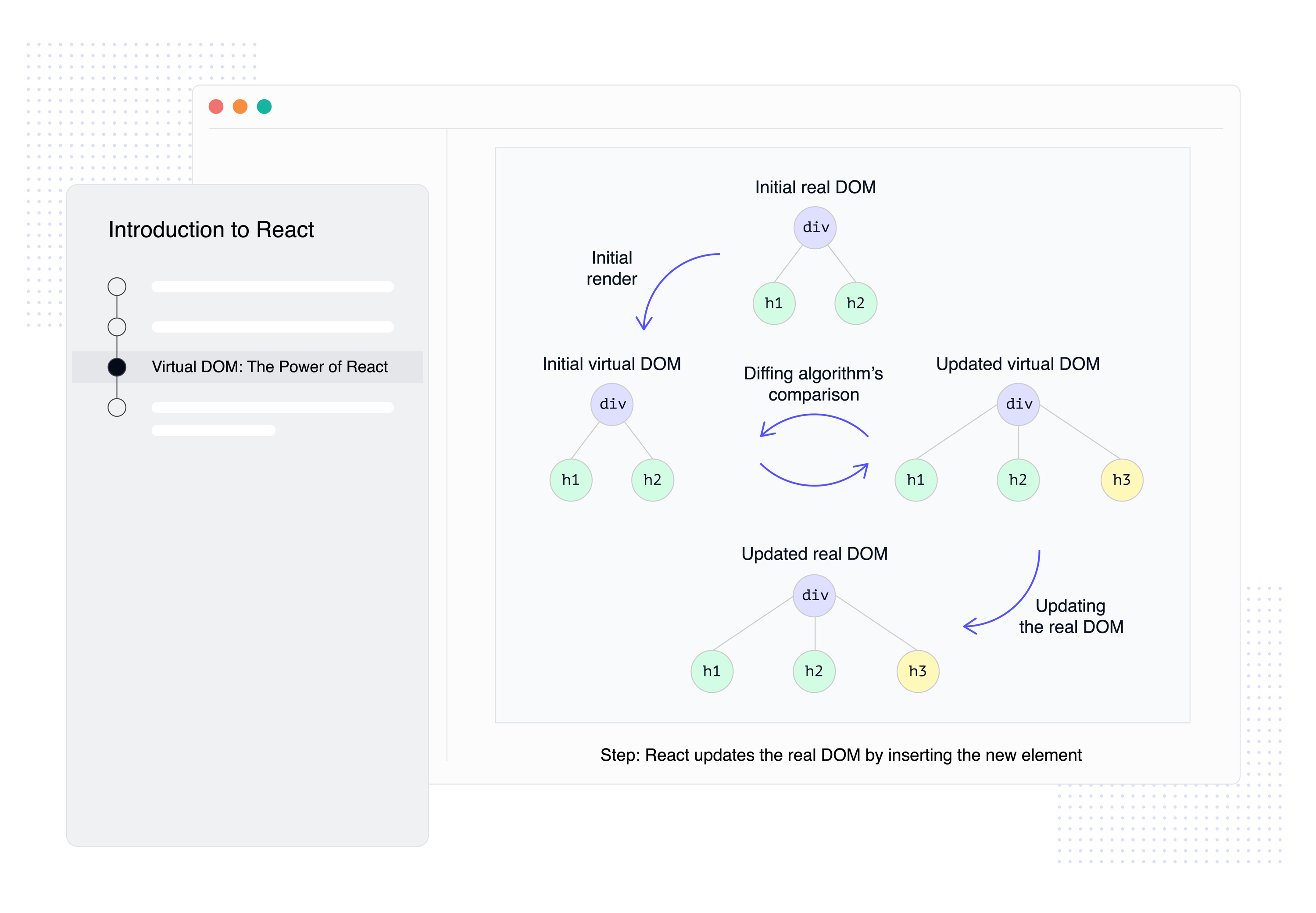
Explore React and its benefits, JSX syntax, virtual DOM, and how to render dynamic elements, laying the groundwork for React development.
4.
React Components
React Components
8 Lessons
8 Lessons
Dive into React components to build dynamic UIs with props, handle events, style components, and create a reusable stateless component.
5.
Hooks: Managing States and Effects in React Components
Hooks: Managing States and Effects in React Components
10 Lessons
10 Lessons
Explore React Hooks like useState, useEffect, useContext, and useMemo to manage state, handle side effects, and optimize performance.
6.
React Router and Navigations
React Router and Navigations
10 Lessons
10 Lessons
Understand React Router essentials, including defining routes, dynamic navigation, nested routes, and handling 404 pages to create seamless SPAs.
7.
New Improvements in React 19
New Improvements in React 19
6 Lessons
6 Lessons
Explore React 19's enhancements for refs, context, metadata, and async scripts.
8.
Advanced Hooks in Practice
Advanced Hooks in Practice
8 Lessons
8 Lessons
Master advanced React Hooks like useReducer, useCallback, useRef, and custom Hooks to optimize performance and reuse logic efficiently.
9.
Concurrency for Smooth UIs
Concurrency for Smooth UIs
7 Lessons
7 Lessons
Learn how React’s concurrency features like useTransition and useDeferredValue make UIs faster, smoother, and more responsive to user interactions.
10.
Handling Forms in React (Controlled and Uncontrolled Components)
Handling Forms in React (Controlled and Uncontrolled Components)
13 Lessons
13 Lessons
Understand how React manages form data using controlled and uncontrolled components to build flexible, reliable, and interactive user input forms.
11.
Data Fetching and API Integration
Data Fetching and API Integration
13 Lessons
13 Lessons
Learn how to fetch, manage, and display data in React using the Fetch API, Axios, or React Query, and how to handle loading states, errors, and caching.
12.
Architecting React Apps at Scale
Architecting React Apps at Scale
15 Lessons
15 Lessons
Master scalable state management in React through effective patterns and architecture.
13.
React 19 Rendering Internals and Performance Optimization
React 19 Rendering Internals and Performance Optimization
13 Lessons
13 Lessons
Optimize React performance through advanced rendering techniques and effective state management strategies.
Certificate of Completion
Showcase your accomplishment by sharing your certificate of completion.
Complete more lessons to unlock your certificate
Developed by MAANG Engineers
Trusted by 2.9 million developers working at companies
"These are high-quality courses. Trust me the price is worth it for the content quality. Educative came at the right time in my career. I'm understanding topics better than with any book or online video tutorial I've done. Truly made for developers. Thanks"
Anthony Walker
@_webarchitect_
"Just finished my first full #ML course: Machine learning for Software Engineers from Educative, Inc. ... Highly recommend!"
Evan Dunbar
ML Engineer
"You guys are the gold standard of crash-courses... Narrow enough that it doesn't need years of study or a full blown book to get the gist, but broad enough that an afternoon of Googling doesn't cut it."
Software Developer
Carlos Matias La Borde
"I spend my days and nights on Educative. It is indispensable. It is such a unique and reader-friendly site"
Souvik Kundu
Front-end Developer
"Your courses are simply awesome, the depth they go into and the breadth of coverage is so good that I don't have to refer to 10 different websites looking for interview topics and content."
Vinay Krishnaiah
Software Developer
Hands-on Learning Powered by AI
See how Educative uses AI to make your learning more immersive than ever before.
AI Prompt
Code Feedback
Explain with AI
AI Code Mentor
Free Resources