Problem Statement#
Given a sorted array of integers, return the low and high index of the given key. You must return -1 if the indexes are not found.
The array length can be in the millions with many duplicates.
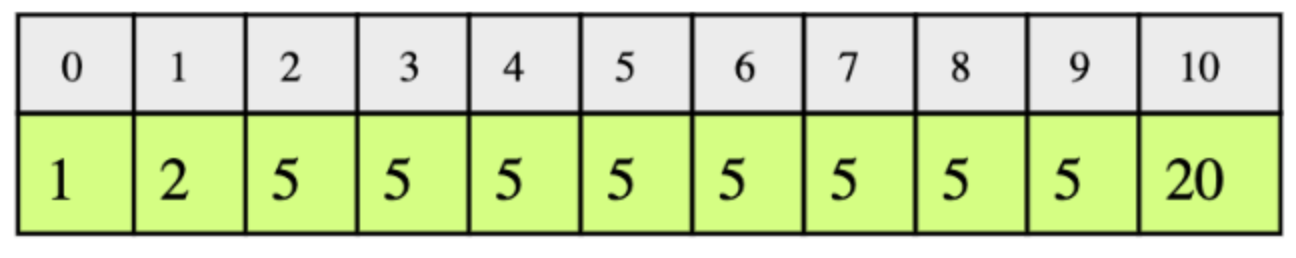
In the following example, according to the the key, the low and high indices would be:
key: 1,low= 0 andhigh= 0key: 2,low= 1 andhigh= 1key: 5,low= 2 andhigh= 9key: 20,low= 10 andhigh= 10
1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3, 4, 4, 4, 4, 5, 5, 5, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6
Solution#
Solution Explanation#
Runtime complexity#
Since we are using binary search, the runtime complexity is logarithmic, O(logn).
Memory complexity#
The memory complexity is constant, O(1) since no extra storage is being used.
Solution Breakdown#
Linearly scanning the sorted array for low and high indices are highly inefficient since our array size can be in millions.
Instead, we will use a slightly modified binary search to find the low and high indices of a given key.
We need to do binary search twice;
once for finding the
lowindex.once for finding the
highindex.
Low index#
Let’s look at the algorithm for finding the low index:
At every step, consider the array between
lowandhighindices and calculate themidindex.If the element at
midindex is less than thekey,lowbecomesmid + 1(to move towards the start of range).If the element at mid is greater or equal to the
key, thehighbecomesmid - 1. Index atlowremains the same.When
lowis greater thanhigh,lowwould be pointing to the first occurrence of thekey.If the element at
lowdoes not match thekey, return-1.
High index#
Similarly, we can find the high index by slightly modifying the above condition:
switch the
lowindex tomid + 1when element atmidindex is less than or equal to thekey.switch the
highindex tomid - 1when the element atmidis greater than thekey.
Practice problems like this and many more by checking out our Grokking the Coding Interview: Patterns for Coding Questions course!