Python—due to its low learning curve, relatively simple syntax, readability, wide applicability, and rich frameworks—is an ideal language for beginners to start learning how to code. These reasons also make Python efficient for game development, no matter the complexity level. Python relies on its various GUI libraries like Tkinter to create the game’s frontend, and its compact yet powerful syntax allow users to write game logic in just a few lines of code. As a result, Python makes game development easy for beginners and pros alike.
Python Tkinter Tutorial: build a jumbled words game from scratch
This article is part of a Python Tkinter series written by Pratik Shukla. And stay tuned for more Tkinker articles from Pratik!
This series aims to introduce you to Tkinter, Python’s standard interface to the Tk GUI toolkit, and help you build interactive games you can add to your resume. To get up to speed on Tkinter, go read our first article in this series Python Tkinter Tutorial: build a number guessing game. Once you get down the basics, come back here to build a jumbled words game from scratch!
Today, we will cover:
- Jumbled words game walkthrough
- Jumbled words game implementation
- Putting it all together
- Wrapping up and resources
Jumbled words game walkthrough#
In this article, we’ll develop a cool game in which our program will generate jumbled words from the list of words provided. The user has to guess the actual word from the jumbled word. Our program will also count the amount of time taken to guess the correct word. Here we will use tkinter module of python to use different widgets like entry, label, and button.
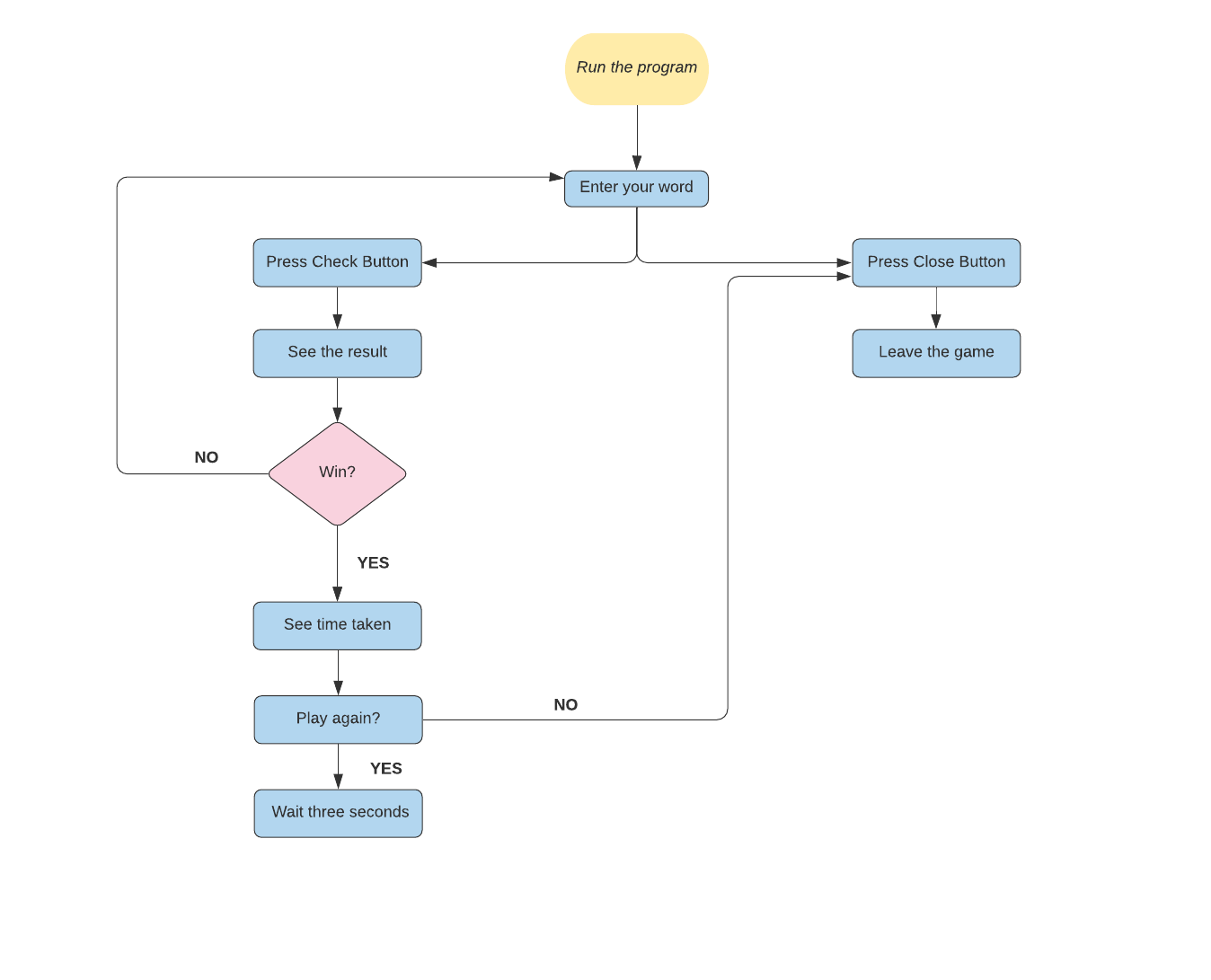
How to play#
- Run the program.
- Enter your guess from jumbled word.
- Check the result.
- Play again or close.
Walkthrough#
When the user runs the program, the user will see a jumbled word on the Tkinter window. Now the user has to guess the actual word from the jumbled word provided and enter their guess in the entry widget. Now, to check if the guessed word was correct, the user has to press the check button.
If the guessed word is correct, the label will transform its image to Win and the correct word will be shown to user. Our program will also show us the time taken by the user to guess the correct word.
If the user’s guess is wrong, then label will show a Lose image, and the entry widget will be cleared for to enter the word again. Our program will not show the correct word or time taken if the user’s guess is wrong.
If the user wants to play the game again, they wait for 3 seconds, and the new window will open with new word. If the user wants to terminate the game, they have to press the close button on the window. Our program will also play different sound files on various events.
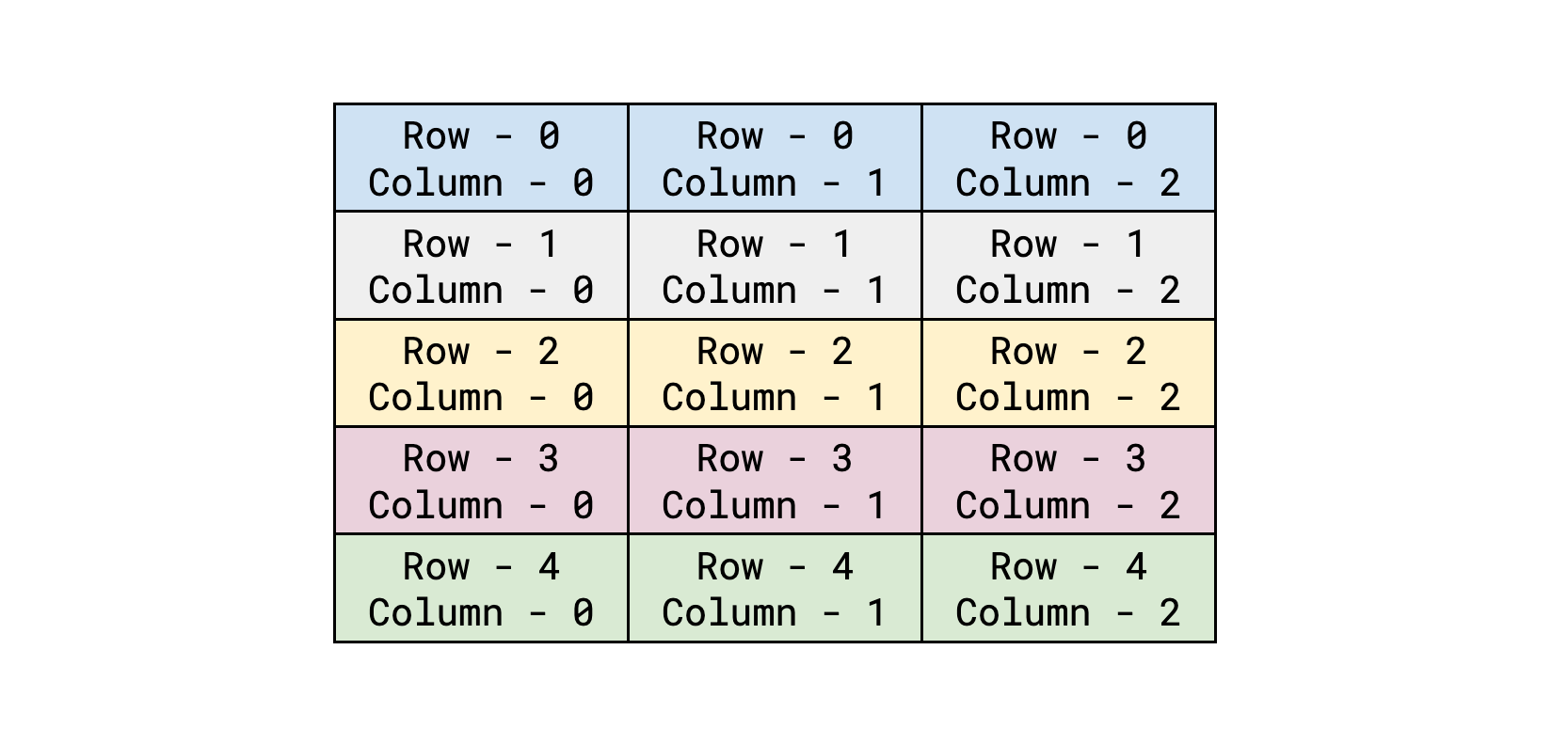
Row-column representation in Tkinter#
Final Result#
Implementation in Python (12 steps)#
Now that we have a sense of what the jumbled words game will entail, let’s walk step-by-step through the process in Python. If you don’t yet know how to set up Tkinter, check out our first article in this series for a brief tutorial.
1. Import required libraries#
tkinter: To add widgets in our applicationsimpleaudio: To play the sound filesrandom: To select a random wordtkinter.font: To change the properties of fonttime: To calculate the time taken by user
2. Create main Tkinter window#
- First we create a variable called
runningand set its value toTrue. Our program will generate a new window when the variable is set toTrue. When the user presses the main close button in title bar, it will exit the loop. root = Tk( ): This is used to initialize our tkinter module.root.title( ): We use it to set the title for our application.root.geometry( ): We use this to specify at which location our application window will open. In our case, it will open at 100 points to the left and 0 points to the down from the top-left corner.root.configure( ): We use this to specify the background color for our application. In our case the background color will be black.root.resizable( ): Here we are using it to prevent the users from resizing our main window.root.iconphoto( ): We are using it to set the icon in the title bar for our application window. We are setting the first parameter toTrue, so that will ensure that all the other windows created from this application has the same icon.- Here we’re also creating a variable called
start time, which stores the time value when the window was opened.
3. Loading sound files#
Now we will use some sound files that will play at various events. When our program starts it will play start file. We’ll play the other three files when the user’s guess is correct, when the user’s guess is wrong and when user closes the application respectively.
One thing to notice is that it only accepts .wav files. First of all we need to load the sound file as an object. Then we can play it using .play( ) method when required.
4. Select a word randomly#
This function will select a word randomly from the list of words provided. It can contain as many words as you want. The random.choice( ) method randomly selects a word from of list of word. Then we’ll return that word to use it in other functions.
5. Jumble the selected word#
Now that our program has selected a word, we need to jumble it for our game. This function takes into input the word selected by our previous function. The random.sample( ) function takes a word, jumbles it, and gives list of letters. We can specify the length of the word, but in our case, it’ll be same as the original word. Then we need to join the jumbled letters to make a string. Finally, it will return the jumbled word so that we can use it in next function.
6. Arrange the letters#
- The randomly selected word will be stored in
pickvariable. - The jumbled word will be stored in
jumbledvariable. List1will convert our string into a list of letters.len_list1gives us the length of the word.- Then we load the images for our letters. Our images are stored as
A_P.png,B_P.png,C_P.png, and so on. - We want the letter images to show as label and it should be on one row. We’ll increase the column values as new letter arrives. The final result will be the jumbled word represented as labels of images.
7. Load other required images#
- After we have added the word, we’ll add a blank row to make it less congested.
- Now, we will modify the fonts to use later in our entry widget.
- Now we need various images for the
main label,win,lose,check,close, etc. So, here we are loading them into variables to use it later.
8. Add Entry widget#
- Now we are going to add a label that says enter your guess. Here we’re using the modified fonts we made in the previous point.
- After that, we are just adding blank space.
- Now we are adding the entry widget, where the user will enter their guessed word. Here we’re using
columnspanto make that into center. - Now we add a blank space again.
9. Original word images#
Now, we need to add the check button and close button. Pressing these buttons will trigger the result( ) and reset( ) functions respectively. The Check button will be on the first column, and the close button will be on the last column.
10. Result and time label#
- Here we’re adding one more label that will display the result for user’s guess.
- We. are also modifying the fonts again to use in the time label. The
timelabel will display the time taken by the user to guess the correct answer.
11. Main function to calculate the decision#
- First, we take the value entered by user in the entry widget.
- Then, we are checking if the word entered by user is correct. If the word is correct, it will calculate the time taken by user to guess the word. Then, it’s going to change the text of time label to display the time taken by user.
- After that, it’s going to play a sound file. Here the label will show the
WINimage. Now we will display the image label for the actual word. Our program will wait for 3 seconds, close the current window, and open a new one. - If the user has entered the wrong word, the label will show
loseimage, and the entry widget will be cleared for user to reenter the word. After 0.5 seconds, theLoselabel will go back to its original image.
12. Reset( ) function and enter the main loop#
- If the user presses the close button, then the
reset( )function will trigger. It will set the running variable toFalseso that our program can’t open a new window. - We then have to enter the main loop to run the program. If our program doesn’t have this line, it will not work.
Putting it all together#
Take a look at the complete code for this Python Tkinter game.
Want to download the code and images? You can download all the necessary images and code here.
Wrapping up and resources#
Congrats! You’ve reached the end and built a successful Python Tkinter game. Great work applying your Python knowledge. I hope you enjoyed this article and learnt something new from it. Python is such an intuitive programming language that the easiest way to master it is through hands-on practice like this. Keep up the work and keep building!
In this series on Tkinter, we’ll be developing a total of Five games using Tkinter. So, hang tight! If you have any doubts, questions, or thoughts regarding this article, feel free to contact me at shuklapratik22@gmail.com
Continue learning#
Frequently Asked Questions
Is Python easy to make games?
Is Python easy to make games?