Serialize/Deserialize Binary Tree
Problem Statement#
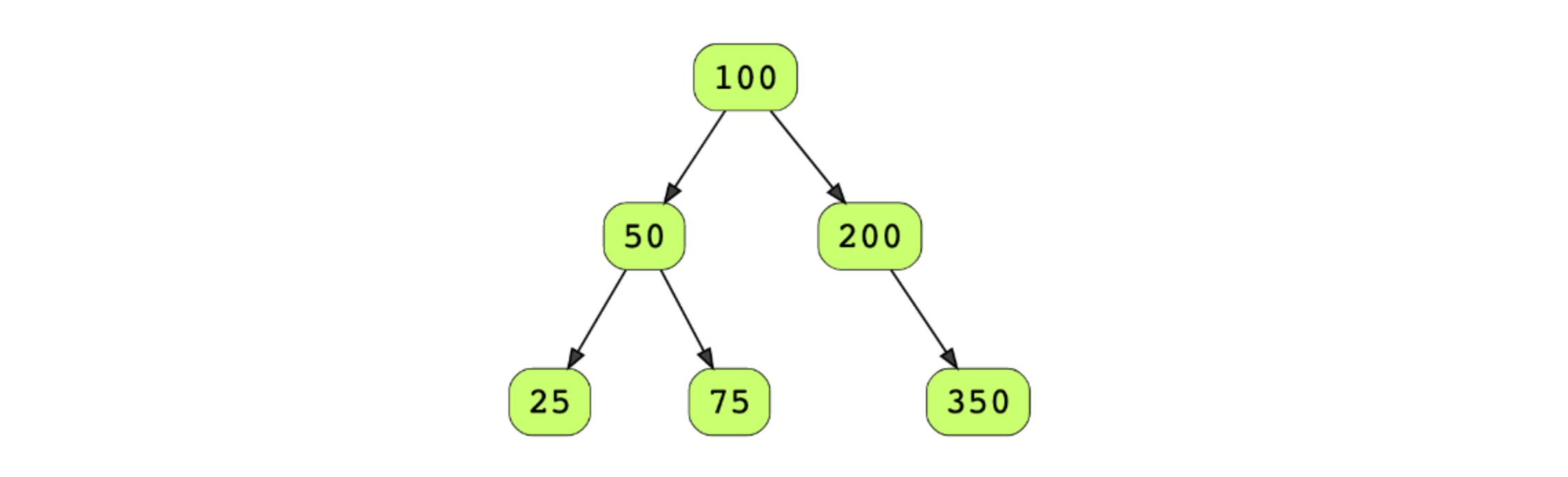
Serialize a binary tree to a file and then deserialize it back to a tree so that the original and the deserialized trees are identical.Serialize: write the tree in a file.Deserialize: read from a file and reconstruct the tree in memory.Consider the below tree as the input tree.
Solution#
Solution Explanation#
Runtime Complexity#
Linear, O(n).
Memory Complexity#
Logarithmic, O(logn).
Recursive solution has O(h) memory complexity as it will consume memory on the stack up to the height of the binary tree h. It will be O(logn) for a balanced tree and in the worst case can be O(n).
Solution Breakdown#
There can be multiple approaches to serialize and deserialize the tree. One approach is to perform a depth-first traversal and serialize individual nodes to the stream. We’ll use a pre-order traversal here. We’ll also serialize some marker to represent a null pointer to help deserialize the tree.
Consider the below binary tree as an example. Markers (M*) have been added in this tree to represent null nodes. The number with each marker i.e. 1 in M1, 2 in M2, merely represents the relative position of a marker in the stream.
The serialized tree (pre-order traversal) from the above example would look like the below list.
When deserializing the tree we’ll again use the pre-order traversal and create a new node for every non-marker node. Encountering a marker indicates that it was a null node.
Practice problems like this and many more by checking out our Grokking the Coding Interview: Patterns for Coding Questions course!