You’ll start Java with the basics, such as printing messages, doing math, and working with user input, before exploring loops, conditionals, and object-oriented programming. Along the way, you’ll build real console apps, like games and menu systems, while learning how to structure your code using classes, methods, and objects. You’ll also practice prompting AI to generate, refine, and debug code, building syntax skills and confidence with AI-enabled workflows.
This course emphasizes hands-on learning and real-world modeling, making Java feel less intimidating and more intuitive. Whether you’re aiming to become an Android developer or backend engineer, or just want a solid foundation in programming, this course will help you write clean, structured code and confidently take your first step into software development. You need to know absolutely nothing about programming before your first lesson.
You’ll start Java with the basics, such as printing messages, doing math, and working with user input, before exploring loops, c...Show More
WHAT YOU'LL LEARN
The ability to write Java programs with logic, input, loops, and structured flow
Hands-on experience building projects using classes, objects, and reusable methods
The ability to create and use classes, objects, methods, and encapsulation
The ability to apply concepts through mini games and projects
Hands-on experience building a strong Java foundation for development in Android, backend, or desktop apps
An experience of how to leverage AI as a work partner
The ability to write Java programs with logic, input, loops, and structured flow
Show more
Learning Roadmap
YOUR ROADMAP
1.
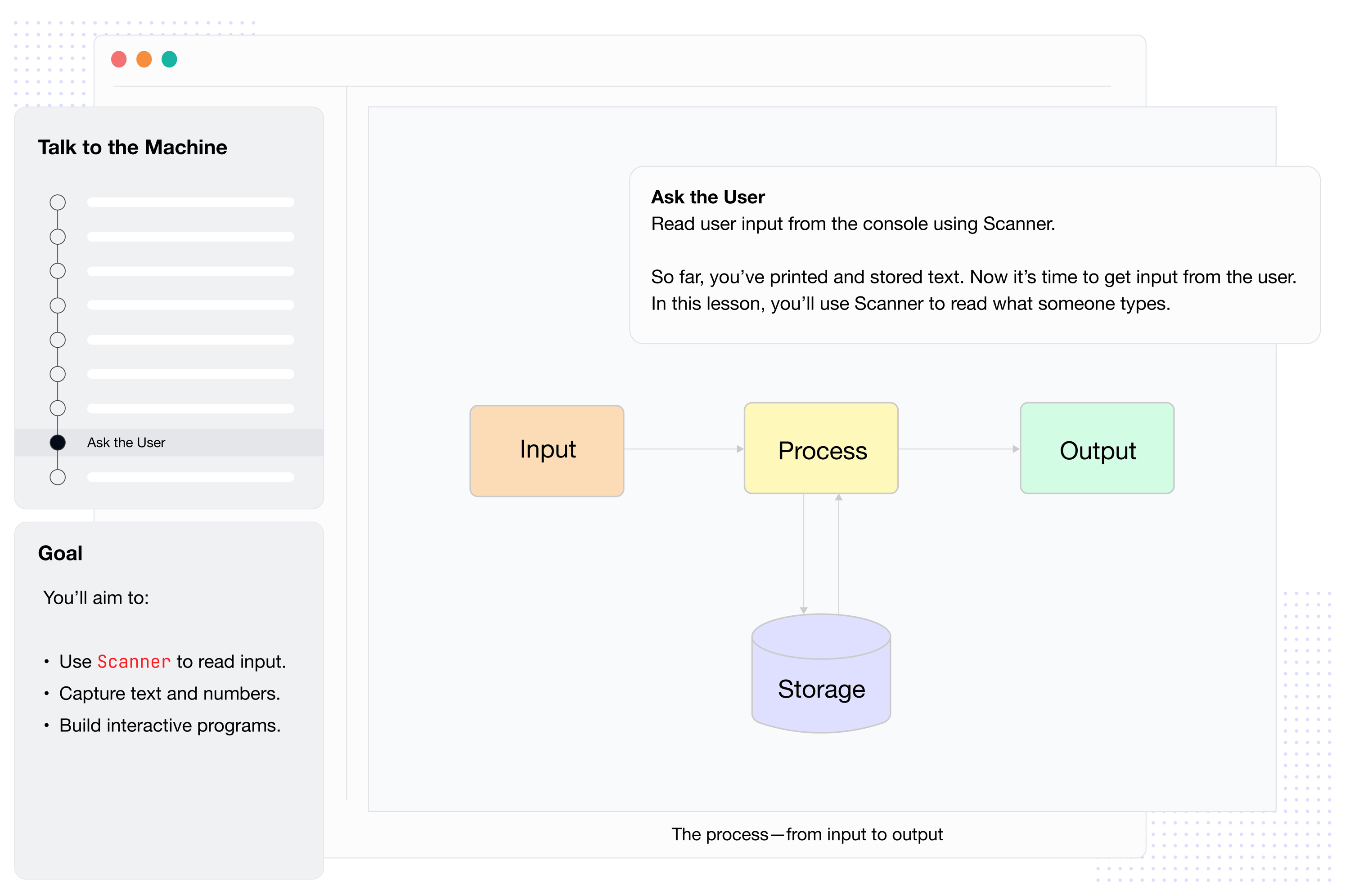
Talk to the Machine
Talk to the Machine
Get Java talking, calculating, and storing values.
Say “Hello, World!”Quiz: “Hello, World!”Challenge: Print More Messages!Do Some MathQuiz: Do Some MathChallenge: Arithmetic OperationsRemember ThingsQuiz: Remember ThingsChallenge: Store Personal Info in JavaWork with the TextQuiz: Work with the TextChallenge: Personalize Your Java OutputAsk the UserQuiz: Ask the UserChallenge: Get to Know the User
2.
Teach It to Think
Teach It to Think
Use logic, branching, and repetition.
3.
Give It Structure
Give It Structure
13 Lessons
13 Lessons
Model your world with classes and methods.
4.
Make It Real
Make It Real
10 Lessons
10 Lessons
Build more complete apps with a real-world structure.
5.
Learn Java in the Age of AI
Learn Java in the Age of AI
6 Lessons
6 Lessons
Build your Java portfolio by creating a Budget Tracker, enhancing coding skills through AI collaboration.
Certificate of Completion
Showcase your accomplishment by sharing your certificate of completion.
Complete more lessons to unlock your certificate
Developed by MAANG Engineers
Trusted by 2.9 million developers working at companies
"These are high-quality courses. Trust me the price is worth it for the content quality. Educative came at the right time in my career. I'm understanding topics better than with any book or online video tutorial I've done. Truly made for developers. Thanks"
Anthony Walker
@_webarchitect_
"Just finished my first full #ML course: Machine learning for Software Engineers from Educative, Inc. ... Highly recommend!"
Evan Dunbar
ML Engineer
"You guys are the gold standard of crash-courses... Narrow enough that it doesn't need years of study or a full blown book to get the gist, but broad enough that an afternoon of Googling doesn't cut it."
Software Developer
Carlos Matias La Borde
"I spend my days and nights on Educative. It is indispensable. It is such a unique and reader-friendly site"
Souvik Kundu
Front-end Developer
"Your courses are simply awesome, the depth they go into and the breadth of coverage is so good that I don't have to refer to 10 different websites looking for interview topics and content."
Vinay Krishnaiah
Software Developer
Hands-on Learning Powered by AI
See how Educative uses AI to make your learning more immersive than ever before.
AI Prompt
Code Feedback
Explain with AI
AI Code Mentor
Free Resources