Problem Statement#
Convert a binary tree to a doubly linked list so that the order of the doubly linked list is the same as an in-order traversal of the binary tree. After conversion, the left pointer of the node should be pointing to the previous node in the doubly linked list, and the right pointer should be pointing to the next node in the doubly linked list.
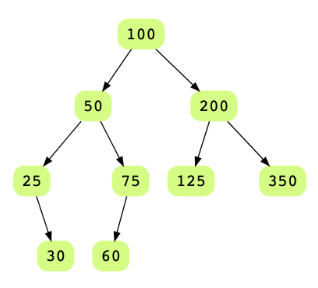
Consider the tree below:
Its in-order traversal will be 25, 30, 50, 60, 75, 100, 125, 200, 350. So, the output doubly linked list should look like so:
Solution#
Solution Explanation#
Runtime Complexity#
Linear, O(n).
Runtime complexity is based on the number of nodes in the tree.
Memory Complexity#
Linear, O(h).
Recursive solution has O(h) memory complexity as it will consume memory on the stack up to the height of binary tree ‘h’. It will be O(log n) for balanced tree and in worst case can be O(n).
Solution Breakdown#
In an in-order traversal, first the left sub-tree is traversed, then the root is visited, and finally the right sub-tree is traversed.
One simple way of solving this problem is to start with an empty doubly linked list. While doing the in-order traversal of the binary tree, keep inserting each element output into the doubly linked list. But, if we look at the question carefully, the interviewer wants us to convert the binary tree to a doubly linked list in-place i.e. we should not create new nodes for the doubly linked list.
This problem can be solved recursively using a divide and conquer approach. Below is the algorithm specified.
Start with the root node and solve left and right sub-trees recursively
At each step, once left and right sub-trees have been processed:
Fuse output of left subtree with root to make the intermediate result
Fuse intermediate result (built in the previous step) with output from the right sub-tree to make the final result of the current recursive call
Practice problems like this and many more by checking out our Grokking the Coding Interview: Patterns for Coding Questions course!
Free Resources