Spring is the most widely used framework for developing Java Enterprise edition applications. Additionally, Spring’s core features apply to any Java application. You can use its extensions to build various web applications on the Jakarta EE platform.
Top 40 Questions for a Spring Framework Interview
The Spring framework makes J2EE (Java 2 Platform Enterprise Edition) development easier and is used to create testable, high performing, reusable code. Spring is commonly applied in the information technologies and financial sector due to its modularity and dependency injection features.
Financial technology is an exciting and evolving field for developers who want to work at companies like MIT, Accenture, or Visa, which prefer Spring over Java EE. These companies are looking for developers like you with Spring Framework experience to help digitize their enterprise needs.
But, how do you know if you’re ready for an interview? And how do you prepare?
Today, we’ll go through a study guide of the top 40 Spring interview questions to make sure you’re ready to ace your Spring Framework interview.
Answer any Java interview problem by learning the patterns behind common questions.
I created Grokking the Coding Interview because I watched too many talented engineers fail interviews they should have passed. At Microsoft and Meta, I saw firsthand what separated the candidates who succeeded from the ones who didn't. It wasn't how many LeetCode problems they'd solved. It was whether they could look at an unfamiliar problem and know how to approach it the right way. That's what this course teaches. Rather than throwing hundreds of disconnected problems at you, we organize the entire coding interview around 28 fundamental patterns. Each pattern is a reusable strategy. Once you understand two pointers, for example, you can apply them to dozens of problems you've never seen before. The course walks you through each pattern step by step, starting with the intuition behind it, then building through increasingly complex applications. As with every course on Educative, you will practice in a hands-on way with 500+ challenges, 17 mock interviews, and detailed explanations for every solution. The course is available in Python, Java, JavaScript, Go, C++, and C#, so you can prep in the language you'll actually use in your interview. Whether you're preparing for your first FAANG loop or brushing up after a few years away from interviewing, this course will give you a repeatable framework for cracking the coding interview.
What is the Spring Framework?#
Spring Framework is an open-source application framework and Inversion of Control container written in Java. It is designed to simplify application design by automatically handling low level functionalities. This allows developers to focus on business logic. Spring is also very adaptable with many extension modules that grow the framework’s capabilities.
While Spring doesn’t impose a specific programming model, it has gained wide popularity in the Java community as an addition to the Enterprise JavaBeans model (EJB). This is in part due to Spring’s unique selection of functionalities like inversion of control and aspect-oriented programming (AOP) that are great for working with beans.
The framework is especially suited for enterprise and financial applications due to its speed, security, and easy-to-build transaction systems. The Spring framework offers many advantages over Java EE or other Java-based frameworks, such as:
-
Spring enables you to develop enterprise-level apps with POJOs, so you don’t need another EJB container product.
-
Spring offers a consistent, scalable transaction management interface for both local transactions and global transactions.
-
Spring is organized in a modular fashion. Its web framework is a lightweight, web MVC framework.
-
Spring makes innovative uses of pre-existing technologies, such as ORM frameworks, JEE, and JDK timers.
-
It is easy to test an application in Spring.
-
Spring provides an excellent API, so it’s easy to work with technology-specific exceptions.
What to expect from a Spring Framework interview#
Most companies looking for Spring Framework expertise are finance companies like banks and investment firms. Some of the top employers of Spring applicants are Citibank, eBay, Visa, and J.P. Morgan.
These companies are interested in using Spring to secure and optimize their accounting and sales stack. Most interview questions will, therefore, test your knowledge of these features like dependency injection, aspect-oriented programming, and MVC.
There will also be general questions to ensure you have a full understanding of each part of Spring, like naming the modules used in web application development or database connectivity.
Finally, you’ll certainly be asked overarching questions about why Spring is used and what benefits it offers.
To help you prepare, we’ve collected 40 top interview questions to refresh your knowledge on each of these categories.
Let’s get started!
Top 40 Questions for Spring Framework:#
1. What are the benefits of Spring?#
- Lightweight: Spring is lightweight in resource use, with the basic Spring Framework only costing 2MB of storage.
- Scalable: Spring’s transaction management interface can scale to either a local transaction on a single database to global transactions using the JTA module
- Exception Handling: Exception handling is easy thanks to plentiful API resources for handling exceptions in each module.
- Layered Architecture: Allows you to use the parts of the program you need and discard the rest.
- POJO Enabled: Plain Old Java Object Programming allows you continuous testability and integration.
- Open-source: Free for everyone and has no vendor lock-in.
- Inversion of control (IOC): Achieves loose coupling via IOC by allowing objects to give their dependencies to other objects rather without dependent objects.
- Aspect oriented (AOP): Spring supports Aspect-oriented programming, a paradigm that separates application business logic from system services.
2. What is the configuration file for Spring?#
The configuration file for Spring is an XML file that contains the class information for a project. They describe the configuration of each class, how they’re introduced to other classes, and dependencies across the program.
3. What are the different modules of Spring Framework?#
There are around 20 modules in total and are divided into the layers of Core Container, Data Access/Integration, Web, AOP (Aspect Oriented Programming), Instrumentation, and Test.
-
Core Container: The core of the Spring Framework contains 4 modules.
- Spring Core
- Spring Bean
- SpEL (Spring Expression Language)
- Spring Context
-
Data Access/Integration: Supports database interactions with 5 modules.
- JDBC (Java DataBase Connectivity)
- ORM (Object Relational Mapping)
- OXM (Object XML Mappers)
- JMS (Java Messaging Service)
- Transaction
-
Web: Adds support for creating a web application using 4 modules.
- Web
- Web – MVC
- Web – Socket
- Web – Portlet
-
Aspect-Oriented Programming: This layer allows you to decouple code using Advice and Pointcut functions.
-
Instrumentation: This layer adds support for class instrumentation and classloader implementations.
-
Test: Adds support for testing using Junit and TestNG.
-
Miscellaneous: 2 modules exist outside of these layer categories.
-
Aspects: Allows Spring to integrate with Aspect.
-
Messaging: Adds support for STOMP, an annotation programming model, and allows you to route STOMP messages from WebSocket clients.
-
4. What are the different components of a Spring application?#
Spring applications contain 5 components:
- Interface: Defines program functions.
- Bean class: Contains properties, setter and getter methods for accessing the bean, and specific functions, etc.
- Spring Aspect-Oriented Programming (AOP): Includes cross-cutting concerns functionality, which is not supported in Object-Oriented Programming.
- Bean Configuration File: Contains the information of classes, how to configure them, and defines their relationships.
- User program: Calls functions across the program
Enjoying the article? Scroll down to sign up for our free, bi-monthly newsletter.
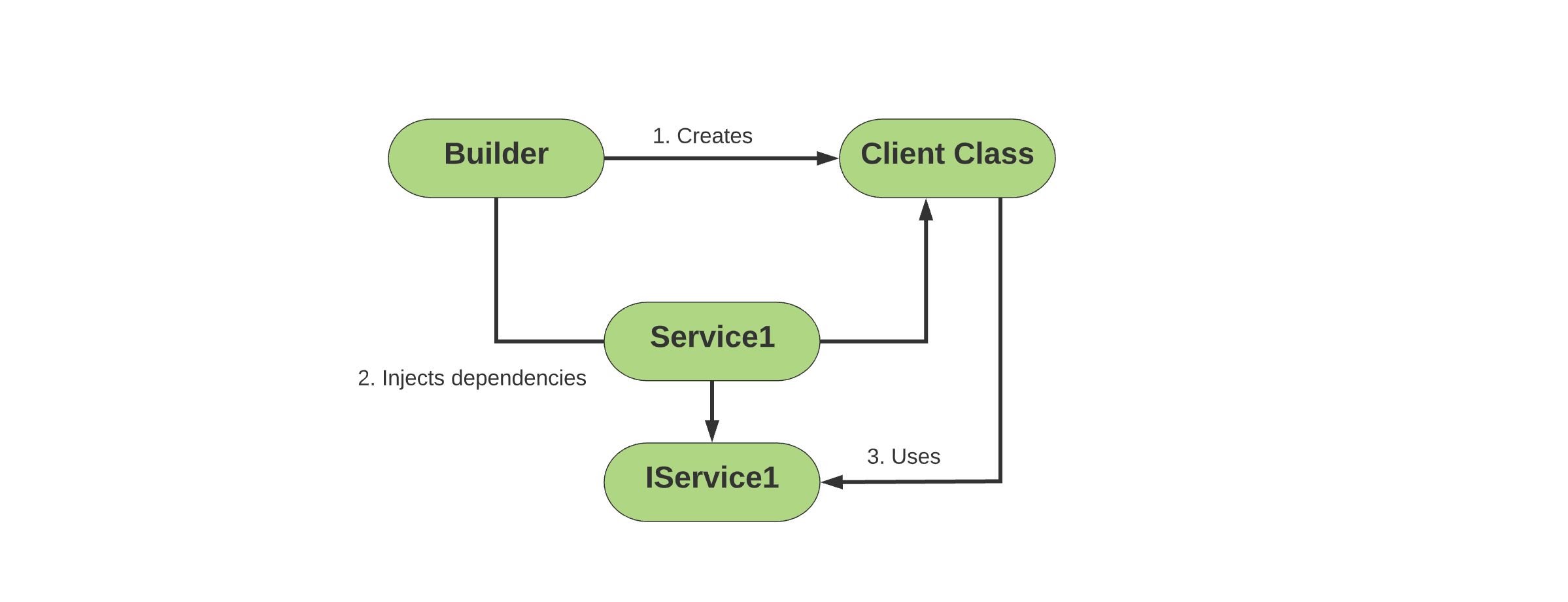
5. What is dependency injection?#
Dependency injection (DI) is a concept that defines how multiple classes should be connected. This is one example of Inversion of Control. You don’t need to connect services and components explicitly in code when using dependency injection. Instead, you describe the services needed by each component in an XML configuration file and allow the IOC container to connect them automatically.
6. What is a Spring IoC container?#
An IoC container creates, configures, and connects objects while also managing their lifecycle. The container gets instructions on these areas from configuration metadata given by the user.
7. What are the types of IoC?#
-
BeanFactory Container: This factory class contains a prepackaged collection of beans that instantiate when called by clients. This is the most basic container to support DI.
-
ApplicationContext Container: Built on top of the BeanFactory Container, this container provides additional enterprise-focused functionalities. For example, ApplicationContext containers grant the ability to resolve textual messages and publish application events.
8. What is Aspect-Oriented Programming (AOP)?#
AOP is a programming technique that allows programmers to modularize behavior that is used across the typical divisions of responsibility found in Object-Oriented Programming. The core AOP construct of aspects are behaviors applicable across classes. Extracting these behaviors from individual beans to aspects allows them to be reused easily.
9. What are Spring beans?#
Beans are objects created from configuration metadata when it is passed to the IOC container. They form the foundation of all Spring programs. The IOC container instantiates, configures, connects, and manages each bean.
10. What are the common implementations of the ApplicationContext?#
Three of the most popular containers are:
- FileSystemXmlApplicationContext: Causes the constructor to load bean definitions from an XML configuration file. Must be pointed to with a full file path.
- ClassPathXmlApplicationContext: This container does the same as the above but does not require a full file path. Instead, you set the
CLASSPATHproperty and allow the container to find theXMLat thatCLASSPATH. - WebXmlApplicationContext: Loads all bean definitions to a web application from an
XMLfile.
11. What is the difference between BeanFactory and ApplicationContext?#
The BeanFactory is a basic, space-efficient container with limited functionality. It is best used for simple tasks or when using low-resource machines.
The ApplicationContext is an advanced, more intensive container with an extended interface and additional capabilities like AOP. This container is best used when you need more functionality than the BeanFactory and have ample resources available on the machine.
12. How do you add a bean in a Spring application?#
We must annotate a method: @Bean annotation. When JavaConfig encounters this method, it will execute that method and register the return value as a bean within a BeanFactory.
package io.educative;
public class User {
private String name;
private String address;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
}
13. What bean scopes does Spring support?#
Spring supports five scopes for beans:
- Singleton: Scopes a bean definition to be restricted to a single instance per Spring IoC container
- Prototype: Scopes a single bean to enable any number of instances.
- Request: Scopes a bean definition to a single HTTP request within an ApplicationContext
- Session: Scopes a bean definition to an HTTP session within an ApplicationContext
- Global-session: Scopes a bean definition to a Global HTTP
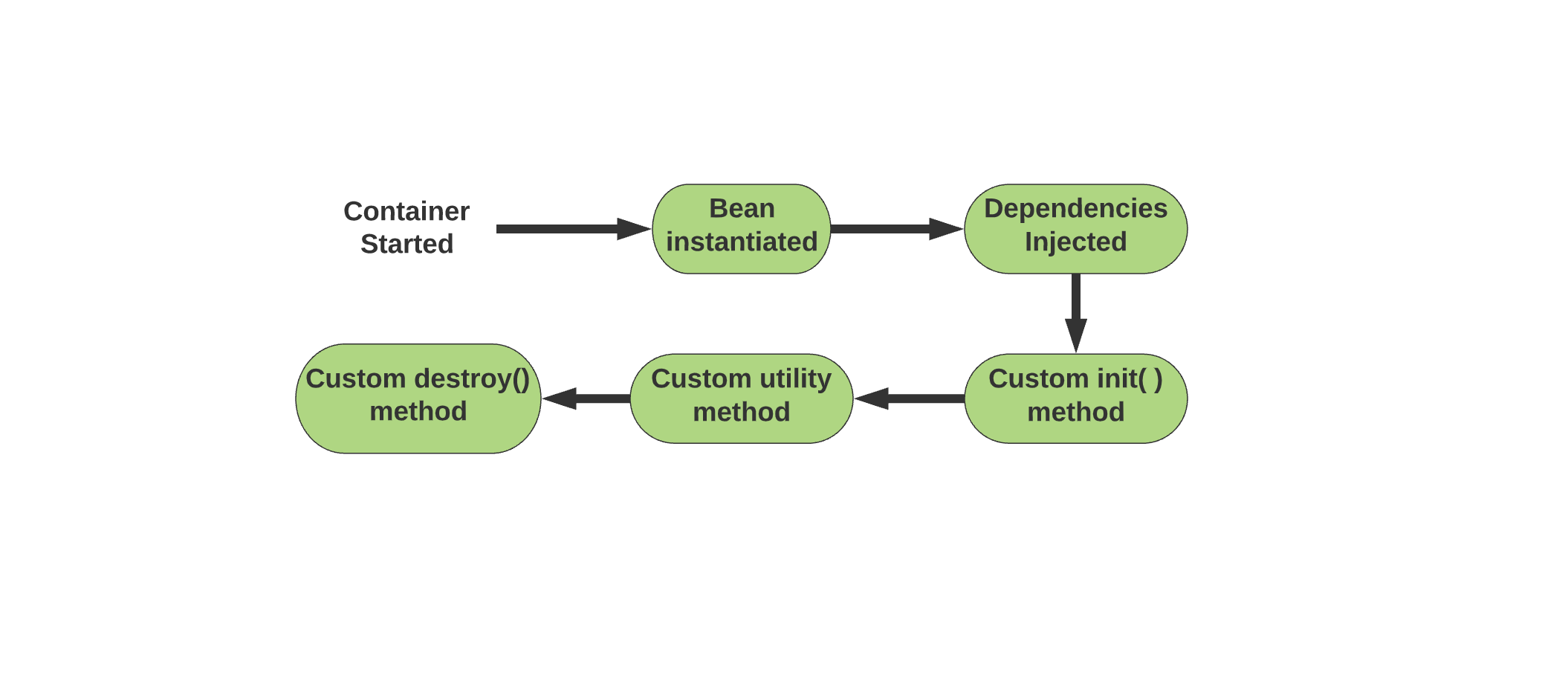
14. What are the steps of the Bean lifecycle?#
There are seven steps to the Bean lifecycle:
- Instantiate: The bean is instantiated by the Spring container using the bean’s definition found in the
XMLconfiguration file. - Populate properties: Spring populates all the defined properties from the
XMLfile using dependency injection. - Set Bean Name: Spring passes the bean’s identifier to the
setBeanName()method If the bean uses theBeanNameAwareinterface. - Set Bean factory: Spring passes the
beanfactoryto thesetBeanFactory()method if the bean is configured to use theBeanFactoryAwareinterface. - Pre Initialization: Spring calls any
BeanPostProcessorsassociated with the bean using thepostProcessorBeforeInitialization()method. - Initialization: The bean is then initialized. Any special initialization process specified in the
init-methodis followed. - Post Initialization: All defined
postProcessAfterInitialization()methods are called. Now the bean is complete. Beans that implementDisposableBeanwill be deleted using thedestroy()after their job is finished.
15. Explain inner beans in Spring.#
An inner bean is used as a property of another bean. Inner beans can be defined in the configuration XML file under either the <property> or <constructor-arg> elements. All inner beans are always scoped as prototype and don’t have identifiers.
16. What is bean auto wiring?#
This is a Spring capability that allows the Spring container to automatically set dependency relationships between collaborating beans by looking at the BeanFactory. Autowiring can be set to define these relationships using the beans’ names or type or even class constructors.
17. How can you inject a Java Collection in Spring?#
Java collections can be injected in four different ways:
-
<list>: Helps you wire sets of values like lists while allowing duplicates. -
<set>: Helps you wire a set of values while avoiding duplicates. -
<map>: Allows you to inject a collection of key-value pairs of any data type. -
<props>: Allows you to inject a collection of key-value pairs with both keys and values of typeString.
18. What is a Joinpoint?#
Joinpoints represent any point in a program where an action is taken. Examples of a joinpoint include when handling an exception or a method is executed. When using AOP, only method executions are joinpoints.
19. What is an Advice in Spring?#
An Advice is the action taken at a given joinpoint. AOP uses an Advice as an interceptor before the method’s execution is complete.
20. What are the types of advice for a Spring Framework?#
- Before: These are advices that execute before the joinpoint methods. They’re marked using the
@Beforeannotation mark. - After returning: These execute after the joinpoint’s method completes executing without issue. They’re marked using the
@AfterReturningannotation mark. - After throwing: These execute only if the joinpoint method ends by throwing an exception. They’re marked using the
@AfterThrowingannotation mark. - After: These execute after a joinpoint method, regardless of how it completes. They’re marked using the
@Afterannotation mark. - Around: These execute before and after a joinpoint and are marked using the
@Aroundannotation mark.
Answer any Java interview problem by learning the patterns behind common questions.
I created Grokking the Coding Interview because I watched too many talented engineers fail interviews they should have passed. At Microsoft and Meta, I saw firsthand what separated the candidates who succeeded from the ones who didn't. It wasn't how many LeetCode problems they'd solved. It was whether they could look at an unfamiliar problem and know how to approach it the right way. That's what this course teaches. Rather than throwing hundreds of disconnected problems at you, we organize the entire coding interview around 28 fundamental patterns. Each pattern is a reusable strategy. Once you understand two pointers, for example, you can apply them to dozens of problems you've never seen before. The course walks you through each pattern step by step, starting with the intuition behind it, then building through increasingly complex applications. As with every course on Educative, you will practice in a hands-on way with 500+ challenges, 17 mock interviews, and detailed explanations for every solution. The course is available in Python, Java, JavaScript, Go, C++, and C#, so you can prep in the language you'll actually use in your interview. Whether you're preparing for your first FAANG loop or brushing up after a few years away from interviewing, this course will give you a repeatable framework for cracking the coding interview.
21. What is Weaving?#
Weaving in Spring is the process of linking elements to other application types or objects to create advised objects. This is done at runtime.
22. Describe Spring DAO support.#
Data Access Object (DAO) support is a set of tools that make it easier to work with data access technologies like Hibernate and JDO with improved consistency. It also catches technology-specific errors automatically. Together these make DAOs easier to work with and allows you to switch between persistence technologies without error.
23. What is the JDBC? Which classes are present in the Spring JDBC API?#
JDBC stands for Java Database Connectivity. It is an application programming interface in Java used to define how a program may access a database. The JDBC API contains:
JdbcTemplateNamedParameterJdbcTemplateSimpleJdbcCallSimpleJdbcInsertSimpleJdbcTemplate
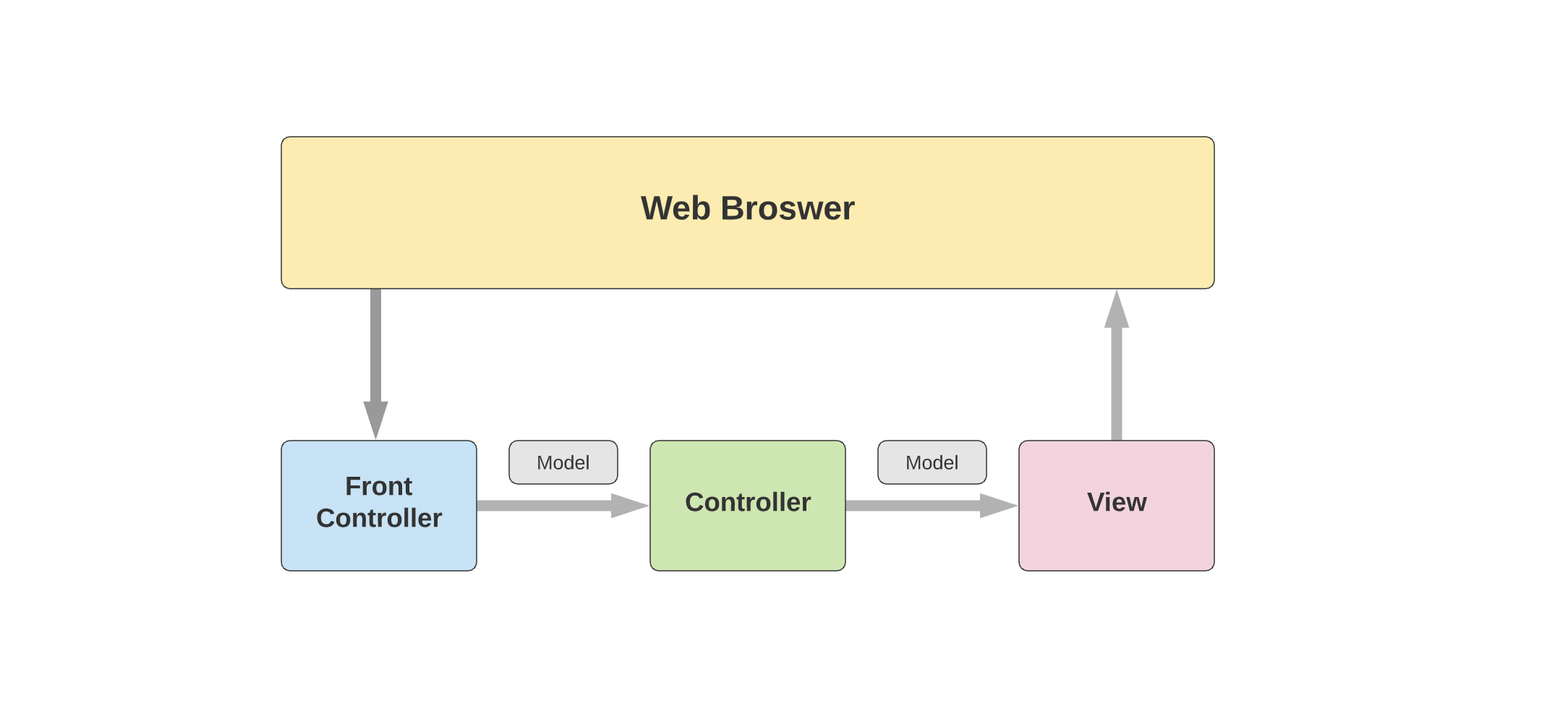
24. What is the Spring Model-View-Controller (MVC) framework?#
The Spring MVC framework provides model-view-controller architecture and premade components used to develop loosely coupled web applications. Using MVC you can separate different aspects of the program like a business, input, and UI logics while still having a loose coupling between each. This allows for greater flexibility in your web applications.
25. What are the parts of Spring MVC framework?#
The 3 main parts of MVC are:
- DispatcherServlet: This part of MVC manages all the HTTP requests, and responses that interact with the program. The
DispatcherServletfirst receives relevant handler mapping from the configuration file and then passes off the request to the controller. TheDispatcherServletis the most important part of the Spring Web MVC framework. - WebApplicationContext: This acts as an extension of the plain ApplicationContext with extra features necessary for web applications. It can uniquely resolve themes and automatically decide which servlet it is associated with.
- Controllers: These are beans within the
DispatcherServletthat act as filters between user input and application response. Controllers take user input, decide if it should be transformed into either a View or a Model, and finally returns the transformed input to the View Resolver for review.
26. What are the different parts of the DispatcherServlet?#
- Handler Mapping: An interface that defines the mapping between handler and request objects. Can be used to create a custom mapping strategy.
- Controller: Determines the app’s response to user input by sorting input requests by their desired outcome. Input is either immediately returned with a View or is transformed into a Model before being passed to the view-resolver.
- View-Resolver: Takes and renders Models from the controller by mapping between View names and actual Views.
27. How can annotation wiring be turned on in Spring?#
To allow annotation wiring, include <context:annotation-config/> in your XML configuration file:
<beans
//...
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
//...
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-2.5.xsd">
//...
<context:annotation-config /> //annotation wiring enabled here
//...
</beans>
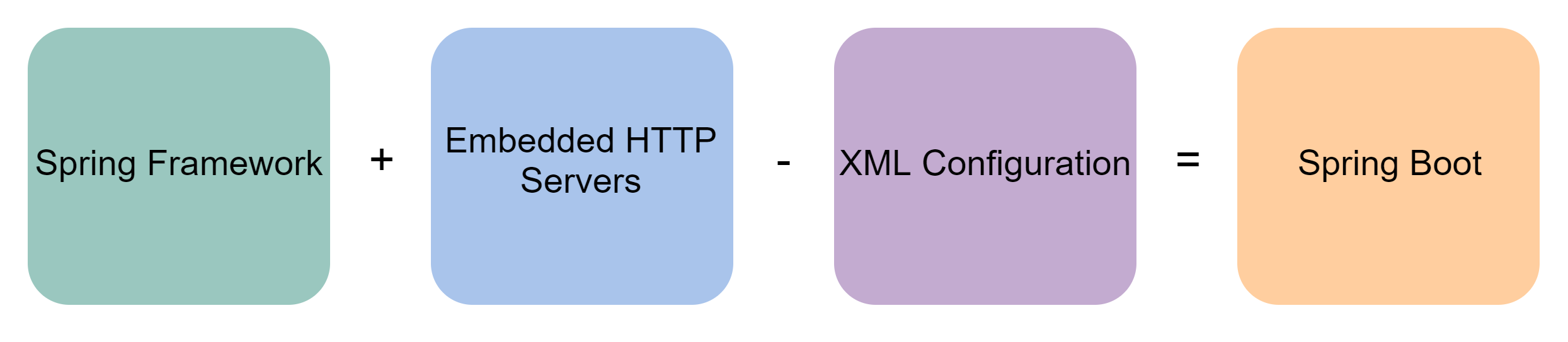
28. What is the Spring Boot?#
Spring Boot is an open-source Java framework used to create microservices. It is a project built on top of Spring to simplify the task of deploying Java applications. Its two major components are the Spring Framework and Embedded HTTP Servers. Spring Boot is used to:
- Simplify the process of developing production-ready Spring applications
- Avoid
XMLconfiguration in Spring - Reduce development time by decreasing the number of needed import statements
- Provide an opinionated development approach
These are often used to get Spring applications running quickly.
29. What is Reactive Programming?#
Reactive Programming is a programming paradigm that relies on programmed actions trigger on events rather than based on the chronological order of the code. Reactive programs make efficient use of computer resources and scale well with just a few threads. Its non-sequential form allows you to avoid stack blocking and maintain responsiveness.
30. What is Spring Webflux?#
Webflux is a reactive web framework that serves as an alternative to MVC. Webflux provides better scalability and prevents stack blocking.
31. What is the difference between the WebClient and Webtestclient?#
The WebClient is a component from the Web Reactive framework that makes it easier to build reactive and non-blocking web applications.
The Webtestclient is a version of this client with all the same features but is disconnected from live environments. The test client doesn’t need an HTTP server live environment to work, making it a good test environment for new applications. It can connect to any server over an HTTP connection or sync directly with WebFlux to apply mock HTTP requests and generate response objects.
32. Can Spring Boot allow Spring MVC or Spring WebFlux in the same application?#
Boot allows both in the same application but can only apply one at a time. WebFlux is a non-blocking framework while MVC is a blocking framework, making them incompatible together.
33. Can Spring 5 Integrate with the Jdk9 Modularity?#
Yes, Spring 5 can integrate with Jdk9. Here’s how you can do it:
- Create a new class
package com.hello;
public class HelloWorld {
public String sayHello(){
return "HelloWorld";
}
}
- Create a new module
module com.hello {
export com.hello;
}
- Create a new Java Project
module com.hello.client {
requires com.hello;
}
- Test the new module
public class HelloWorldClient {
public static void main(String[] args){
HelloWorld helloWorld = new HelloWorld();
log.info(helloWorld.sayHello());
}
}
34. What is a Proxy in Spring?#
A Proxy is an object created after applying advice to a target object. Proxies are used to perform meta-programming operations like intercepting an object call or altering an object’s property.
35. When is the target object and proxy object the same?#
This is a “gotcha” question used to test if you know how different object types interact. The target and proxy objects are the same when dealing with client objects.
36. How can configuration metadata be provided to the Spring container?#
XML-Based Configuration: This type of configuration stores all of a program’s bean definitions and dependencies in an XML file. These files are imported by providing a full file path, like on line 1 below.
<bean id="bean1" class="io.Educative.firstSpring.Bean1">
<property name="name" value="Educative"></property>
</bean>
Annotation-Based Configuration: You can instead create annotations on a class, method, or field in a bean to position it within a component class.
<beans>
<context:annotation-config/>
<!-- bean definitions go here -->
</beans>
Java-Based Configuration: This type of configuration allows you to skip <bean> syntax and instead use the @Bean tag to achieve the same thing. You can also create configuration classes with the @Configuration tag, allowing you to create dependencies between beans by calling other@Bean classes.
@Configuration
public class BeanConfig
{
@Bean
public Bean1 myBean()
{ return new Bean1(); }
}
37. What are the possible exceptions that can be thrown by Spring DAO classes?#
DataAccessResourceFailureExceptionCleanUpFailureDataAccessExceptionInvalidDataAccessApiUsageExceptionInvalidDataAccessResourceUsageExceptionUncategorizedDataAccessExceptionDataIntegrityViolationExceptionDeadLockLoserDatAccessExceptionOptimisticLockingFailureEexceptionIncorrectUpdateSemanticsDataAccessExceptionTypeMismatchDataAccessExceptionObjectRetrievalFailureExceptionDataRetrievalFailureException
38. What are the ways Hibernate can be accessed using Spring?#
Hibernate ORM is an object-relational mapping framework for Java. It is used with Spring to map object-oriented domain models to a relational database. Hibernate can be accessed in Spring in the following two ways:
- First, extend
HibernateDAOSupportand then apply an AOP Interceptor node - Use Inversion of Control with Hibernate Template and Callback structures
39. Point out the difference between concern and cross-cutting concern in Spring AOP?#
A concern is the target functionality we’re trying to implement into a particular module of our application.
A cross-cutting concern is a concern that is used across the entire application rather than just in a particular module.
Data logging is a good example of a cross-cutting concern as logging is useful and desired regardless of what module it is in.
40. What are the types of transaction management available in Spring?#
Declarative transaction management: This type manages transactions using annotations or XML configurations to separate transaction management from the program’s business code. While easy to maintain, this style is more restricted in its capabilities.
Programmatic transaction management: This type manages transactions with specifically made programs. The customization of these programs allows for more flexible management but introduces more room for error in the process.
Wrapping up and what to learn next#
Congratulations on completing these 40 Spring Framework interview questions. As with any interview, success in a Spring interview comes down to your preparation, practice with a variety of interview questions, experience with Spring projects, and familiarity with behavioral interview tips.
Even if you don’t get an offer your first time around, the experience and exposure will help you stand out when you reapply. The most important thing is to stay confident and trust that you deserve this job! Some projects you can explore to put your Spring knowledge into practice are:
- Agile Express
- Spring PetClinc
- Tudu Lists
- Spring Rich Client
- Java Small Business Platform
To start preparing for your Spring interview, be sure to brush up on your Java skills. Educative’s course Grokking Coding Interview Patterns will help you simplify your Java review. You’ll learn the 24 patterns behind every coding interview question, so you can be prepared to answer any problem you might face.
From all of us here at Educative, good luck, and happy learning!
Continue reading about Java and Interview Preparation#
Frequently Asked Questions
How to explain Spring Framework in an interview
How to explain Spring Framework in an interview