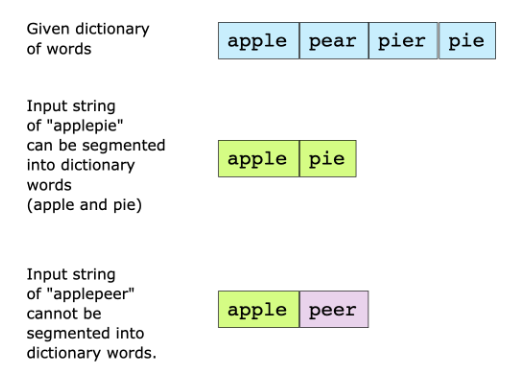
Problem Statement#
You are given a dictionary of words and a large input string. You have to find out whether the input string can be completely segmented into the words of a given dictionary. The following two examples elaborate on the problem further.
Solution#
Solution Explanation#
Runtime Complexity#
The runtime complexity of this solution is polynomial, O(n3)O(n3).
Memory Complexity#
The memory complexity of this solution is linear, O(n)O(n).
Solution Breakdown#
The algorithm iteratively checks substrings of the input string against the dictionary. Starting with an empty string being segmentable, it gradually builds up segmentability information for larger substrings by considering all possible substrings and checking if they exist in the dictionary. Once we determine that a substring can be segmented into words from the dictionary, we mark the corresponding entry in an array dp array as TRUE. Subsequently, when processing longer substrings, we use dp to check whether shorter substrings within them have already been determined to be segmentable, avoiding recomputations.
Initialize a variable
nwith the length of the input word and create a boolean arraydpwith a size ofn + 1. Initialize all values ofdpto FALSE.Set
dp[0]to TRUE to indicate that the empty string can be segmented.Iterate over the indexes of the word from 1 to
n.For each index
i, iterate over the indexesjfrom 0 toi - 1.Check if
dp[j]is TRUE and if the substringword[j:i]exists in the dictionary.If both conditions are met, set
dp[i]to TRUE.After completing the iterations, return
dp[n]to indicate whether the entire word can be segmented.
Practice problems like this and many more by checking out our Grokking the Coding Interview: Patterns for Coding Questions course!
Free Resources