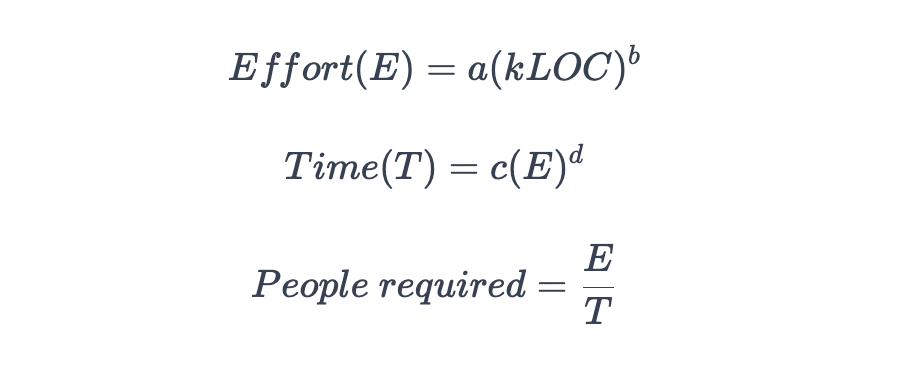The COCOMO model#
COCOMO stands for the constructive cost model, a cost estimation model for software projects based on LOC.
The COCOMO model calculates a proposed software project's time, effort, cost, and quality. In simple words, it predicts the performance of a software project.
Types of software projects#
The COCOMO model can be applied to three types of software projects:
Organic project: An organic software project requires a small team, the problem is well understood, and the team members are experienced in developing similar projects.
Semi-detached project: A semi-attached project is medium-sized, with the development consisting of a mix of experienced and inexperienced staff, and the major characteristics of the project lie in between organic and embedded.
Embedded project: An embedded software project has a high level of complexity, requiring a large-sized experienced team, and is coupled with complex hardware.
Types of COCOMO models#
The COCOMO model is divided into three types based on the accuracy quotient.Any of the three types can be adapted according to our requirements:
Basic model
Intermediate model
Detailed model
Basic model#
The basic model is used for quick and rough cost calculations for the software. It calculates the effort, time, and number of people required to use a project's kLOC (kilo lines of code).
The formulae to calculate these entities are:
The effort is measured in person-months and time in months. The constants
Project Type | a | b | c | d |
Organic | 2.4 | 1.05 | 2.5 | 0.38 |
Semi-detached | 3.0 | 1.12 | 2.5 | 0.35 |
Embedded | 3.6 | 1.20 | 2.5 | 0.32 |
Example#
Suppose a project was estimated to be made in 400 kLOC. Lets calculate its effort, time, and the number of people required while considering the project is of organic type:
Calculate with Cocomo basic calculator#
Now, let's predict the performance of a software project with a cocomo basic calculator.
Intermediate model#
The intermediate model is an extension of the basic model and includes a set of cost drivers to calculate the estimates with better accuracy. The effort factor includes the effort adjustment factor (EAF) that is calculated with the cost drivers.
The formulae to calculate these entities are:
The effort is measured in person-months and time in months. The constants
Project Type | a | b | c | d |
Organic | 3.2 | 1.05 | 2.5 | 0.38 |
Semi-detached | 3.0 | 1.12 | 2.5 | 0.35 |
Embedded | 2.8 | 1.20 | 2.5 | 0.32 |
Hardware attributes#
The hardware attributes are as follows:Run time performance constraintsMemory constraintsThe volatility of the virtual machine environmentRequired turnabout time
Personal attributes#
The personal attributes are as follows:
Analyst capabilities
Software engineering capabilities
Applications experience
Virtual machine experience
Programming language experience
Project attributes#
The project attributes are as follows:
Use of software tools
Application of software engineering methods
Required development schedule
The EAF is calculated by multiplying the parameter values of different cost driver attributes. Ideally, the value is 1.
Example#
Suppose a project was estimated to be made in 400 kLOC.let's calculate its effort, time, and the number of people required while considering the project is of organic type and has a nominal complexity. The developer has a high virtual machine experience.
The value of the nominal complexity of a project is 1.00, and the high virtual experience of the developer is 0.90, according to the tables mentioned above:
Calculate with Cocomo intermediate calculator#
Now, let's predict the performance of a software project with cocomo intermediate calculator.
Detailed model#
The detailed model is a combination of both the basic model and the intermediate model. The model is decomposed into multiple modules, and the COCOMO model is applied to them individually. This model uses various effort multipliers for each cost driver attribute, and the cost is calculated at each stage separately.
The six stages of the detailed model are as follows:
Planning and requirements
System design
Detailed design
Module code and test
Integration and test
Cost constructive model
Conclusion#
The COCOMO model provides a good rough estimation of the cost of the project and the time taken to complete it. Still, it also has limitations as it ignores the factors like customer skills and knowledge. Moreover, in real life, things may not work out according to the model, and the project may take more time than the estimated time and affect the project.
Free Resources