Intermediate
26h
Updated yesterday
Grokking Modern System Design Interview
Everything you need for Grokking the System Design Interview, developed by FAANG engineers. Master distributed system fundamentals and practice real-world interview questions.
WHAT YOU'LL LEARN
Show more
Learning Roadmap
1.
Introduction
Introduction
2.
System Design Interviews
System Design Interviews
3.
Preliminary System Design Concepts
Preliminary System Design Concepts
4 Lessons
4 Lessons
4.
Non-Functional System Characteristics
Non-Functional System Characteristics
7 Lessons
7 Lessons
5.
Back-of-the-Envelope Calculations
Back-of-the-Envelope Calculations
2 Lessons
2 Lessons
7.
Domain Name System
Domain Name System
2 Lessons
2 Lessons
8.
Load Balancers
Load Balancers
3 Lessons
3 Lessons
9.
Databases
Databases
5 Lessons
5 Lessons
10.
Key-Value Store
Key-Value Store
5 Lessons
5 Lessons
11.
Content Delivery Network (CDN)
Content Delivery Network (CDN)
7 Lessons
7 Lessons
12.
Sequencer
Sequencer
3 Lessons
3 Lessons
13.
Distributed Monitoring
Distributed Monitoring
3 Lessons
3 Lessons
14.
Monitor Server-Side Errors
Monitor Server-Side Errors
3 Lessons
3 Lessons
15.
Monitor Client-Side Errors
Monitor Client-Side Errors
2 Lessons
2 Lessons
16.
Distributed Cache
Distributed Cache
6 Lessons
6 Lessons
17.
Distributed Messaging Queue
Distributed Messaging Queue
7 Lessons
7 Lessons
18.
Pub-Sub
Pub-Sub
3 Lessons
3 Lessons
19.
Rate Limiter
Rate Limiter
5 Lessons
5 Lessons
20.
Blob Store
Blob Store
6 Lessons
6 Lessons
21.
Distributed Search
Distributed Search
6 Lessons
6 Lessons
22.
Distributed Logging
Distributed Logging
3 Lessons
3 Lessons
23.
Distributed Task Scheduler
Distributed Task Scheduler
5 Lessons
5 Lessons
24.
Sharded Counters
Sharded Counters
4 Lessons
4 Lessons
25.
Concluding the Building Blocks Discussion
Concluding the Building Blocks Discussion
4 Lessons
4 Lessons
26.
Design YouTube
Design YouTube
6 Lessons
6 Lessons
27.
Design Quora
Design Quora
5 Lessons
5 Lessons
28.
Design Google Maps
Design Google Maps
6 Lessons
6 Lessons
29.
Design a Proximity Service/Yelp
Design a Proximity Service/Yelp
5 Lessons
5 Lessons
30.
Design Uber
Design Uber
7 Lessons
7 Lessons
31.
Design Twitter
Design Twitter
6 Lessons
6 Lessons
33.
Design Instagram
Design Instagram
5 Lessons
5 Lessons
36.
Design WhatsApp
Design WhatsApp
6 Lessons
6 Lessons
37.
Design Typeahead Suggestion
Design Typeahead Suggestion
7 Lessons
7 Lessons
38.
Design a Collaborative Document Editing Service/Google Docs
Design a Collaborative Document Editing Service/Google Docs
5 Lessons
5 Lessons
39.
Design a Deployment System
Design a Deployment System
2 Lessons
2 Lessons
40.
Design a Payment System
Design a Payment System
2 Lessons
2 Lessons
41.
Design a ChatGPT System
Design a ChatGPT System
2 Lessons
2 Lessons
42.
Design a Data Infrastructure System
Design a Data Infrastructure System
3 Lessons
3 Lessons
43.
Spectacular Failures
Spectacular Failures
4 Lessons
4 Lessons
44.
Concluding Remarks
Concluding Remarks
2 Lessons
2 Lessons
45.
Free System Design Lessons
Free System Design Lessons
14 Lessons
14 Lessons
46.
System Design Case Studies
System Design Case Studies
5 Lessons
5 Lessons
Course Author:
Trusted by 2.9 million developers working at companies
Yichen Wang
Software Engineer @ Microsoft
Mike Rabatin
Learner
Kshitij Tiwari
Arachnomesh Technologies
Abhishek R
Learner
JR
Learner
Svitlana Valko
Learner
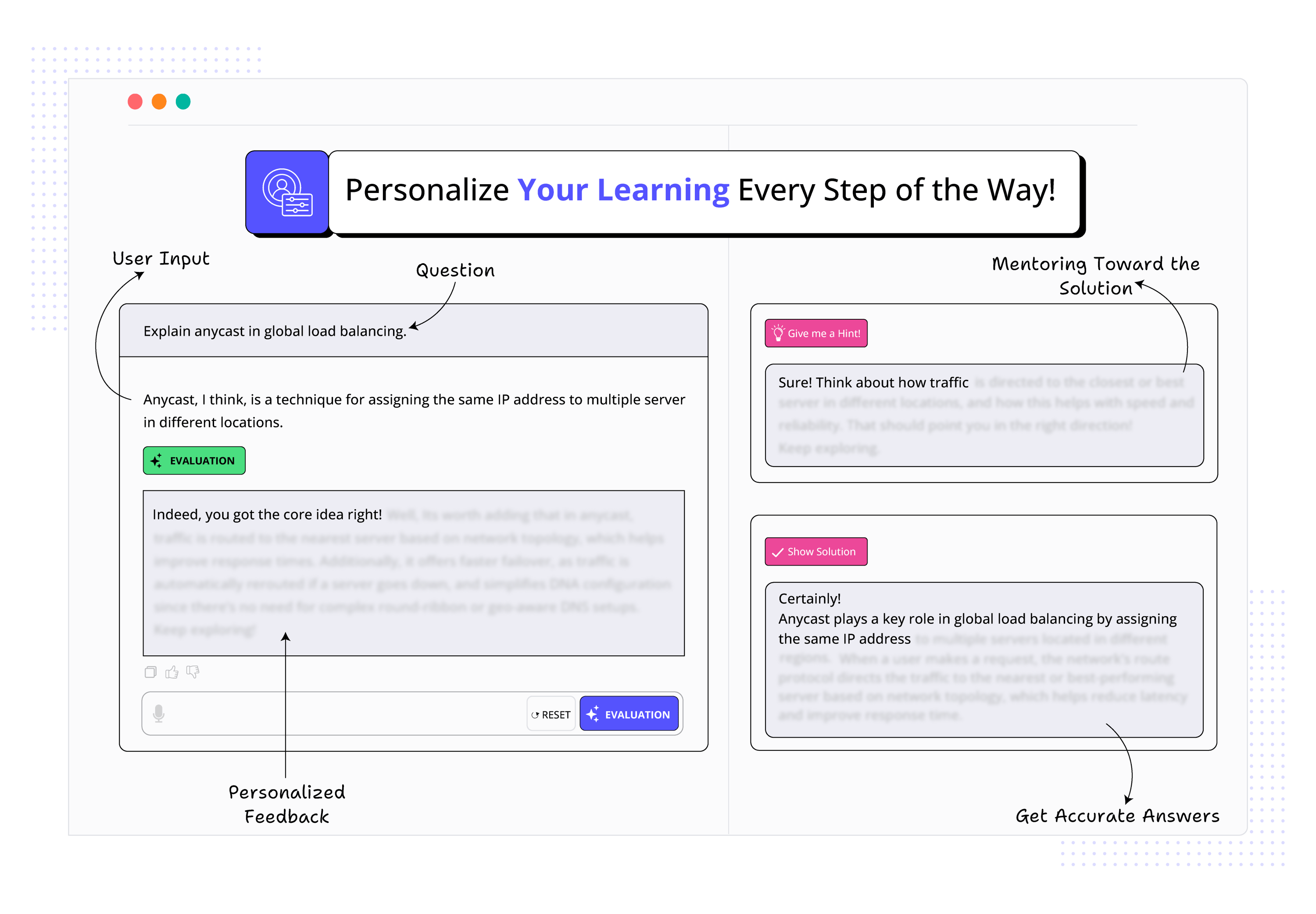
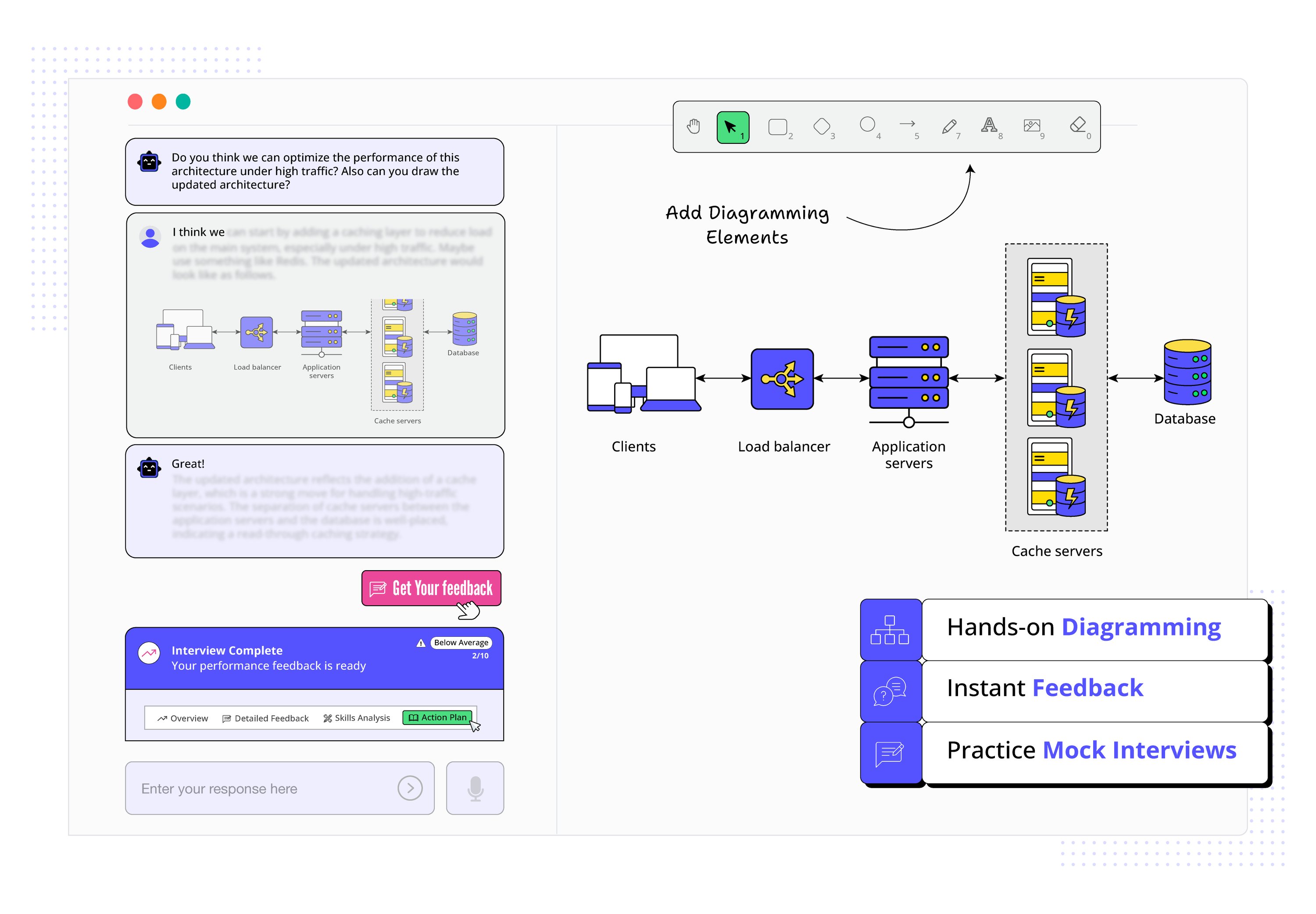
See how Educative uses AI to make your learning more immersive than ever before.
AI Prompt
Code Feedback
Explain with AI
AI Code Mentor
Free Resources
cheatsheet
cheatsheet
cheatsheet
blog
guide